
Preliminary assessment of the acid sulphate soils hazard in the Auckland region New Zealand
This spatial dataset identifies areas of land showing the extent of acid sulfate soils. Acid sulfate soils have been classified into 5 different classes based on the likelihood of the acid sulfate soils being present in particular areas and at certain depths. \\r\\n\\r\\n* Class 1: Acid sulfate soils in a class 1 area are likely to be found on and below the natural ground surface. \\r\\n.

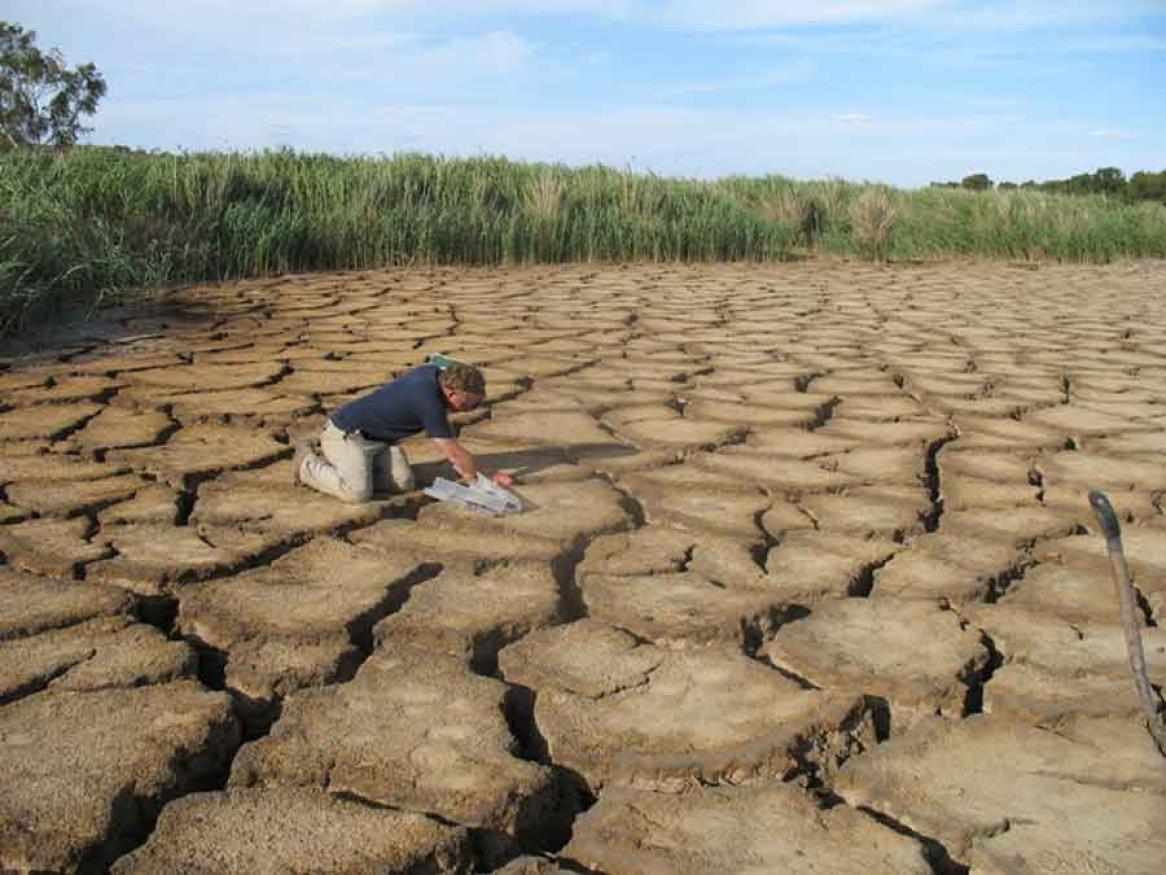
Photograph of a typical acid sulfate soil in an exposed dry river bed... Download Scientific
This spatial dataset identifies areas of land showing the extent of acid sulfate soils. Acid sulfate soils have been classified into 5 different classes based on the likelihood of the acid sulfate soils being present in particular areas and at certain depths. Class 1: Acid sulfate soils in a class 1 area are likely to be found on and below the.
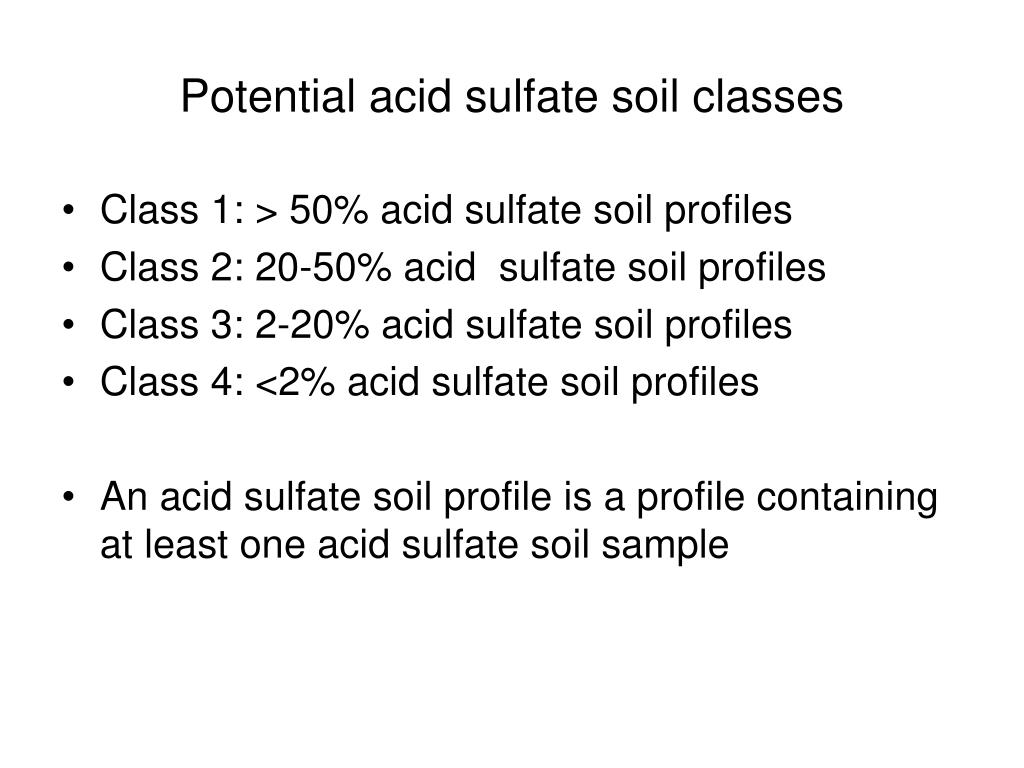
PPT Potential acid sulfate soil PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1831104
Acid sulfate soils have been classified into 5 different classes based on the likelihood of the acid sulfate soils being present in particular areas and at certain depths. Class 1: Acid sulfate soils in a class 1 area are likely to be found on and below the natural ground surface. Class 2 : Acid sulfate soils in a class 2 area are likely to be.

Basic properties of acid sulphate soil Download Scientific Diagram
Soil is a finite natural resource and is indispensable for human civilization because it is the medium for food production for the biosphere. Continued soil degradation is a forerunner of catastrophe for the living world. The protection of healthy soils and the restoration of problem soils are strongly needed in the current agricultural scenario as competition for urbanization and other human.

(PDF) Acid Sulfate Soils Research Program Summary Report Rob Fitzpatrick Academia.edu
The classification of acid sulfate soils is determined based on the levels of certain elements present in the soil as well as the degree of acidity. To facilitate this classification process, the Australian National Committee on Soil and Terrain has developed a system that categorises acid sulfate soils into four distinct classes. This system.

Definition And Causes of Acidic Soil Niche Agriculture
of at least 0.05 per cent serves to distinguish acid sulphate soils from other severely acid soils. This is a broader definition than that adopted by the USDA Soil Taxonomy (Soil Survey Staff 1975), which defines a diagnostic sulfuric horizon by a pH (1:l in water) of less than 3.5 and jarosite mottles. A prime distinction must be made between.

Soil is the topmost layer of the continental crust having weathered particles of rocks. The
Acid sulfate soils can form in parts of inland Queensland where there are appropriate conditions (listed above)—e.g. some of the salt lakes in western Queensland have acid sulfate soils present. Around 35,000 years ago, the sea level in Queensland was higher and large swamps existed in many places along the coast. Since then, the sea has.

National Acid Sulfate Soils Guidance Guidance for the Dewatering of Acid Sulfate Soils in
Acid sulfate soil classification according to the most recent classification proposed for boreal acid sulfate soils (Boman et al., 2018). In situ pH is the lowest pH in the soil profile measured immediately in the field. Incubation pH is the pH of the underlying reduced zone after being incubated (exposed to oxygen) in the laboratory.

Figure 1 from Classification of Acid Sulfate Soils of Peninsular Malaysia Semantic Scholar
Acid sulfate soils have been classified into 5 different classes based on the likelihood of the acid sulfate soils being present in particular areas and at certain depths. Class 1: Acid sulfate soils in a class 1 area are likely to be found on and below the natural ground surface. Class 2 : Acid sulfate soils in a class 2 area are likely to be.

PPT Acid Sulfate Soils Project Experience and L essons Learned Stafford County, VA PowerPoint
An Acid Sulfate Soil Management Plan must be prepared. Sample depths are to exceed 1m beyond the depth of the proposed excavation/disturbance or 2m below existing ground level (whichever is greater). Identify if acid sulfate soils will not be disturbed. If so, an Acid Sulfate Soils Management plan is not required.

Acid sulfate soils explained Environment, land and water Queensland Government
Acid sulfate soils form when sulfide minerals, such as pyrite, and/or elemental sulfur in reduced sulfidic sediments oxidize upon exposure to air. If sulfide-bearing subaqueous soils are dredged and placed in a subaerial environment, sulfides will oxidize, creating sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid will drastically lower soil pH (to less than 4.

Basic Properties of Acid Sulfate Soil Download Scientific Diagram
of their geomorphology, acid sulfate soils can be saline as well. Including 12-13 M ha acid sulfate soils, the global expanse of acid soils is 3950 M ha. Approximately 50% of the world's potentially arable lands are acidic. Selection of suitable crops, liming and other inputs including fertilizers, irrigation and drainage

(PDF) Effects of live wetland plant macrophytes on acidification, redox potential and sulphate
The nastiest soils "Acid sulfate soils are the nastiest soils in the world. They generate sulphuric acid that brings their pH as low as 2 and leaks into drainage and floodwaters. In this acid environment, aluminium and other toxic elements kill vegetation and aquatic life or, in sub-lethal doses, render many species stunted and sickly.

Acid Sulfate Soils Alkalinity Concrete
Acid sulfate soils are naturally occurring soils, sediments or organic substrates (e.g. peat) that are formed under waterlogged conditions.These soils contain iron sulfide minerals (predominantly as the mineral pyrite) and/or their oxidation products. In an undisturbed state below the water table, acid sulfate soils are benign. However, if the soils are drained, excavated or otherwise exposed.

Acid Sulfate Soils Centre University of Adelaide
Acid sulfate soils may affect more than 260,000 hectares of land. About 150,000 hectares of this land are in agricultural production. The largest areas are the coastal floodplains of northern NSW, particularly those of the Tweed, Richmond, Clarence, Macleay and Hastings rivers. Other notable locations include the Hunter and Shoalhaven rivers.

Books UPM Acid Sulfate Soils in Malaysia
This webpage explains what acid sulfate soils are, how to identify them, the impact, how to manage them and the state legislation, policies and risk assessments associated with acid sulfate soils.. Soil classification in Western Australia (Webpage) Waterlogging (Webpage) Water availability in soils (Webpage) Explore More. Disclaimer: This is.
- Words Starting With N To Describe Someone Positively
- Burger Burger Burger Burger Burger Burger
- Lord Of The Rings Concert Melbourne
- Athol Bay Sydney Harbour Map
- Apple Store External Hard Drive
- 12 Casino Rise Prospect Vale
- How Much Does A 2 Coin Weight
- Doctors For The Environment Australia
- 22 24 Martin Road Centennial Park
- Stable Diffusion Image To Image