
Wolff Parkinson White Wpw Syndrome
adults, the prevalence of WPW syndrome is estimated to be 1-3 in 1000 individuals [6]. A higher prevalence of 0.55% has been reported in first-degree relatives of patients with accessory pathways [7]. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is more commonly diagnosed in men than in women, although this sex difference is not observed in children.

WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome WPW is a congenital GrepMed
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a heart condition present at birth. That means it's a congenital heart defect. Researchers aren't sure what causes most types of congenital heart defects. WPW syndrome may occur with other congenital heart defects, such as Ebstein anomaly. Rarely, WPW syndrome is passed down through families.

WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome (WPW) Causes, Mechanism, ECG Findings and diagnosis, Treatment
Background: Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a relatively common arrhythmia affecting ~1-3/1,000 individuals. Mutations in PRKAG2 have been described in rare patients in association with cardiomyopathy. However, the genetic basis of WPW in individuals with a structurally normal heart remains poorly understood.

"WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome" by Dr. Gary Dhillon for OPENPediatrics YouTube
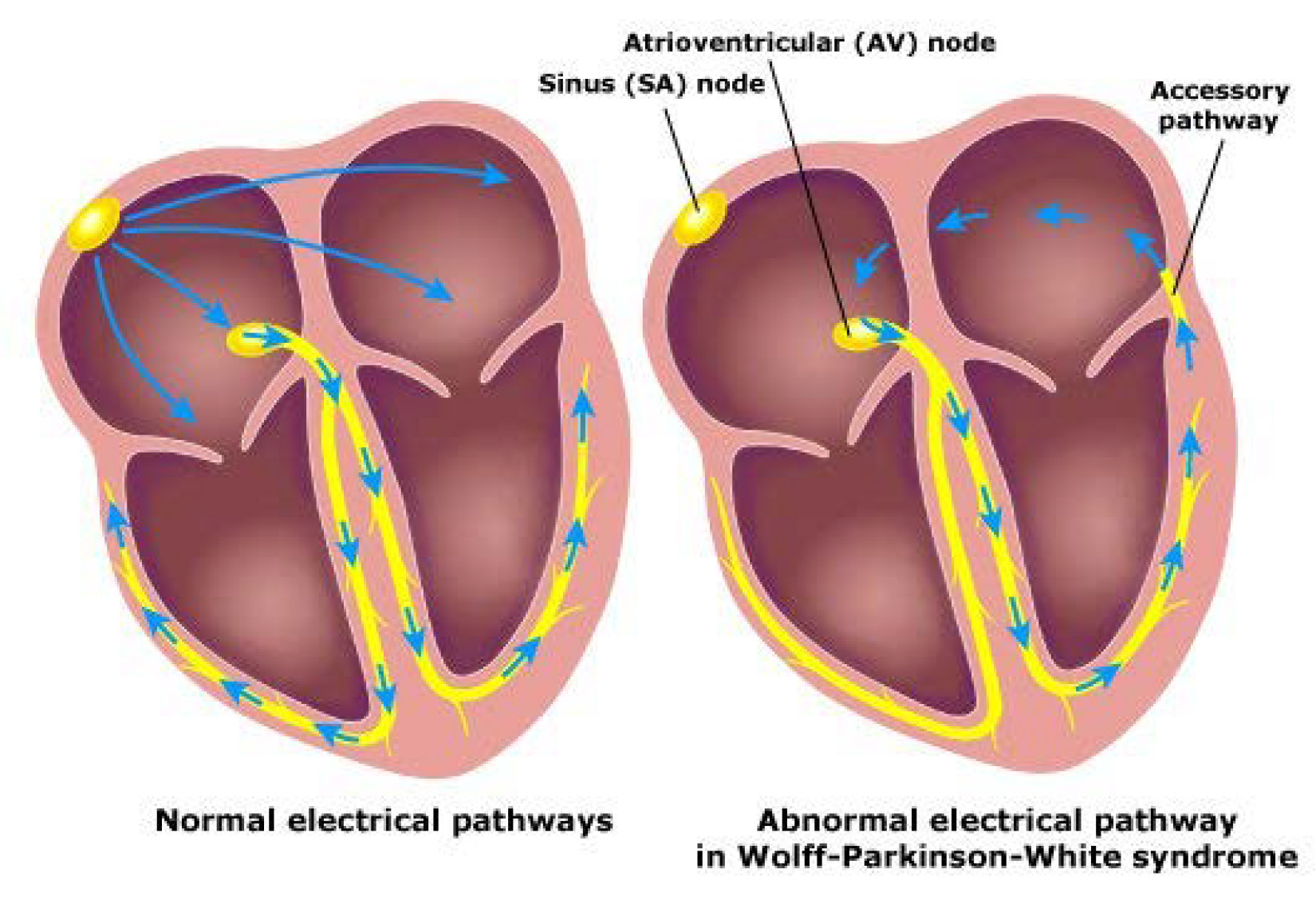
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) is when the heart has an extra electrical pathway, also called an accessory pathway. Because of this extra pathway, electrical signals in the heart avoid the normal electrical pathway. This can lead to life-threatening heart rhythm problems. In WPW, children are usually born with the extra pathway.
WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome illustration EroFound
Wolfe-Parkinson-White Syndrome A Guide for Patients and Health Care Providers How is WPW inherited, and who in a known or suspected family should be tested? WPW is not generally thought to be a genetic or heritable disorder. However, some familial studies have shown an incidence of 5.5/1000 patients among first-degree relatives

Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a type of abnormal heartbeat. If you have WPW, you may have episodes of tachycardia, when your heart beats very rapidly. WPW affects one to three of every 1,000 people worldwide. Electrical signals going through your heart in an organized way control your heartbeat.

WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome Shown Using Medical Animation
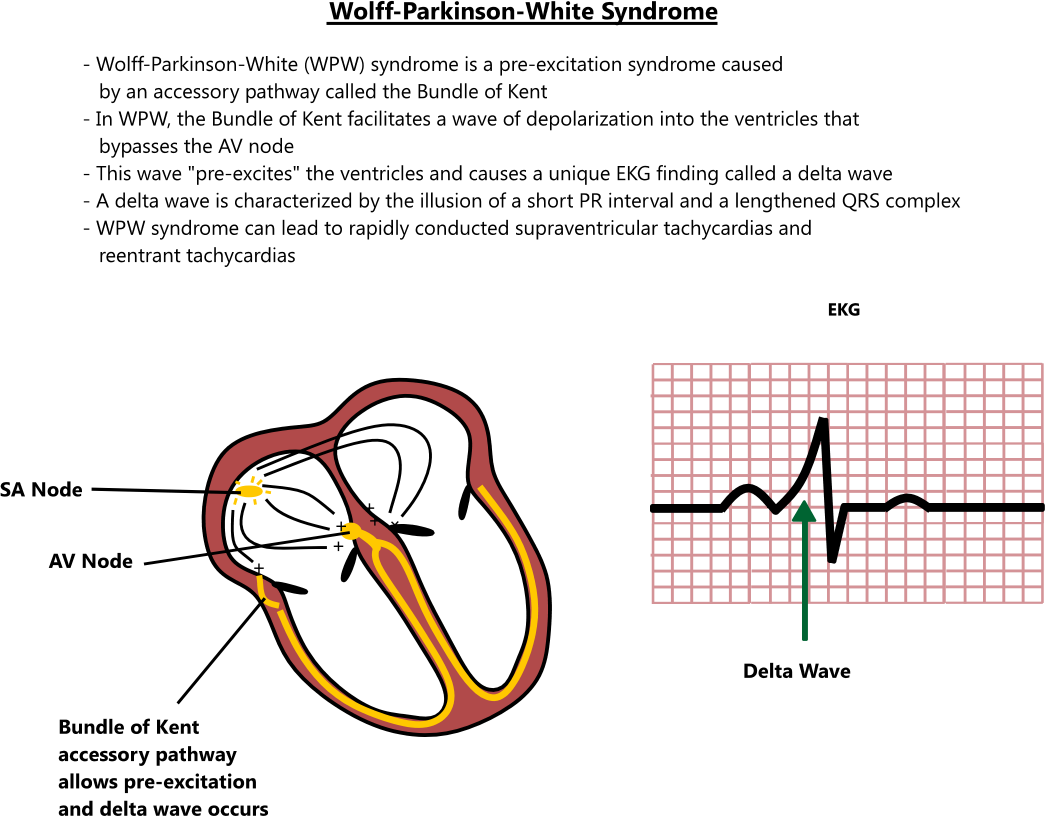
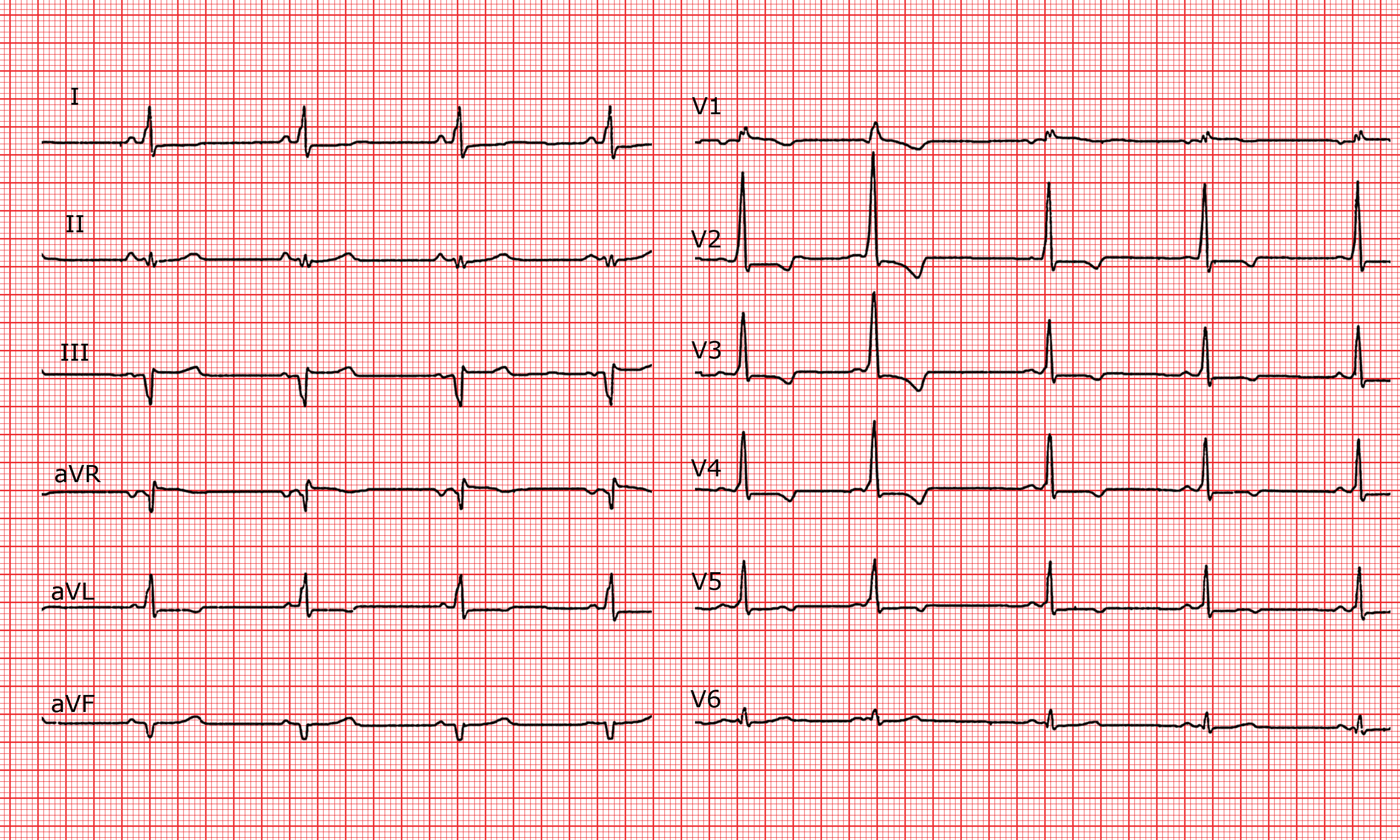
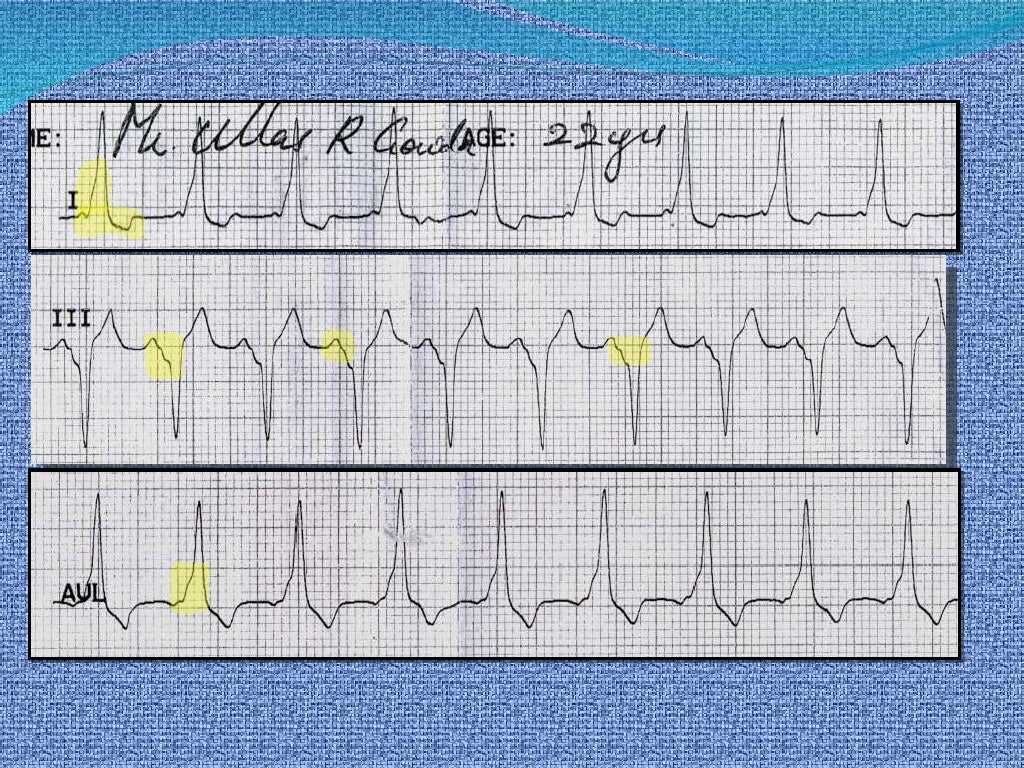
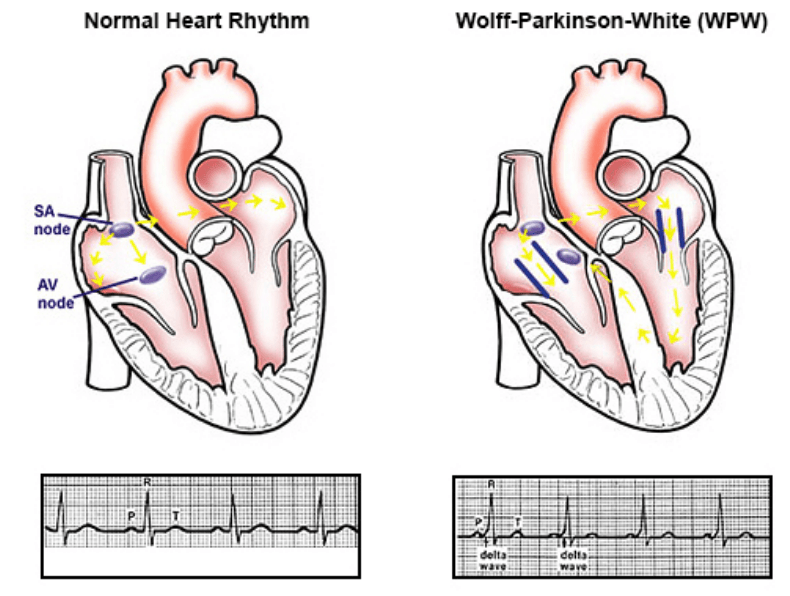
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a congenital cardiac preexcitation syndrome that arises from abnormal cardiac electrical conduction through an accessory pathway that can result in symptomatic and life-threatening arrhythmias. The hallmark electrocardiographic (ECG) finding of WPW pattern or preexcitation consists of a short PR interval and prolonged QRS with an initial slurring.

WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome EKG examples wikidoc
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is associated with several types of arrhythmias (electrical problems of the heart), including supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and pre-excited atrial fibrillation, conditions in which the heart beats abnormally fast. WPW is present at birth and occurs when there is an extra electrical pathway present in.

Concealed WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome revealed by acute coronary syndrome Castro 2020
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a heart condition that occurs in people born with an extra electrical pathway for heartbeat signals. When electrical impulses or signals take this extra route instead of the usual one, they travel through your heart too quickly. This causes your heart to beat rapidly, a type of abnormal heart rhythm that.

WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome (WPW) Study Card Pathophysiology GrepMed
Description. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a condition characterized by abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause a disruption of the heart's normal rhythm (arrhythmia). The heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals that move through the heart in a highly coordinated way. A specialized cluster of cells called the.
[CardioFR] WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome.
A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is caused by heterozygous mutation in the gamma-2 regulatory subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (PRKAG2; 602743) on chromosome 7q36. Mutation in the PRKAG2 gene can also cause a form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in which some patients exhibit WPW (CMH6; 600858).

(A) WolffParkinsonWhite (WPW) syndrome (pink arrow Delta wave). (B)... Download Scientific
In 1930, Dr Louis Wolff, Sir John Parkinson, and Paul Dudley White described a case series of 11 patients with a syndrome that now bears their name. 1 The first patient with a short PR interval, ventricular preexcitation, and supraventricular tachycardia was described by Cohn and Fraser in 1913. 1 Wood et al postulated the accessory pathway (AP) as its anatomic substrate in 1942, and a large.
ECG WolffParkinsonWhite syndrome
Wolf-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a disorder characterized by the presence of at least one accessory pathway (AP) that can predispose people to atrial/ventricular tachyarrhythmias and even sudden cardiac death. It is the second most common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in most parts of the world, affecting about 0.1-0.3%.

WolffParkinsonWhite Syndrome Pathophysiology, PreExcitation and AVRT, Animation YouTube
The history of the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a 50-year-long tale of speculation and discussion among physiologists,. The first 4 exons are missing in PRKAG2b and contain several myrisylation sites and 1 glycosylation domain, which suggests a membrane-bound position for the PRKAG2a protein. Whether the 2a and 2b proteins have.
About Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Hope For Hearts
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPWS) is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart involving an accessory pathway able to conduct electrical current between the atria and the ventricles, thus bypassing the atrioventricular node. About 60% of people with the electrical problem developed symptoms, which may include an abnormally fast heartbeat.
WolffParkinsonWhiteSyndrom (WPWSyndrom) Marienhospital Aachen GmbH
Approximately 10 percent of patients with Ebstein's anomaly have Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome [11,12,13]. Other congenital heart diseases associated with this syndrome include atrial and ventricular septal defects, coronary sinus diverticula, and corrected transposition of the great vessels [ 11 ].