
PPT Physical Geography PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6620772
In physical geography and physical geology, aspect (also known as exposure) is the compass direction or azimuth that a terrain surface faces . For example, a slope landform on the eastern edge of the Rockies toward the Great Plains is described as having an easterly aspect. A slope which falls down to a deep valley on its western side and a.

What is Geography? Teaching Resources
Slope, Aspect, and Hillshade. Slope is the steepness or the degree of incline of a surface. Slope cannot be computed from the lidar points directly; one must first create either a raster or TIN surface. Then, the slope for a particular location is computed as the maximum rate of change of elevation between that location and its surroundings.

What is Physical Geography? YouTube
One of the hardest terms for students new to geographic information systems to understand is the meaning and application of Aspect. When taking one's first steps in spatial analysis using data.
What is Geography Definition of Geography
Learning Objectives. The objective of this section is to describe and discuss the concepts of map scale, coordinate systems, and map projections and explain why they are central to maps, mapping, and geographic information systems (GISs). All map users and map viewers have certain expectations about what is contained on a map.
6th Grade Language Arts Geography Physical Features Map
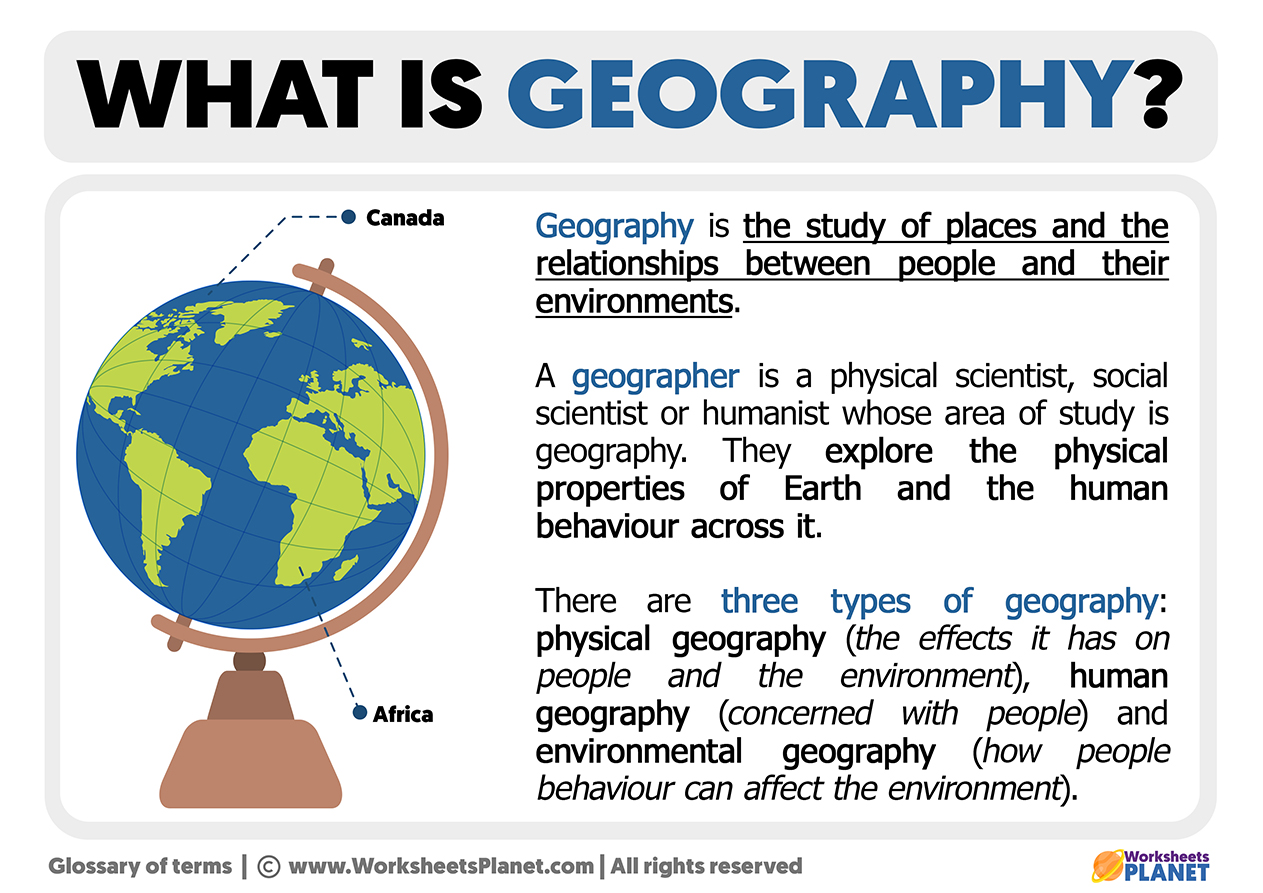
geography, the study of the diverse environments, places, and spaces of Earth's surface and their interactions. It seeks to answer the questions of why things are as they are, where they are. The modern academic discipline of geography is rooted in ancient practice, concerned with the characteristics of places, in particular their natural environments and peoples, as well as the relations.

Geography 7 Introduction to GIS Lab 6 DEM Analysts
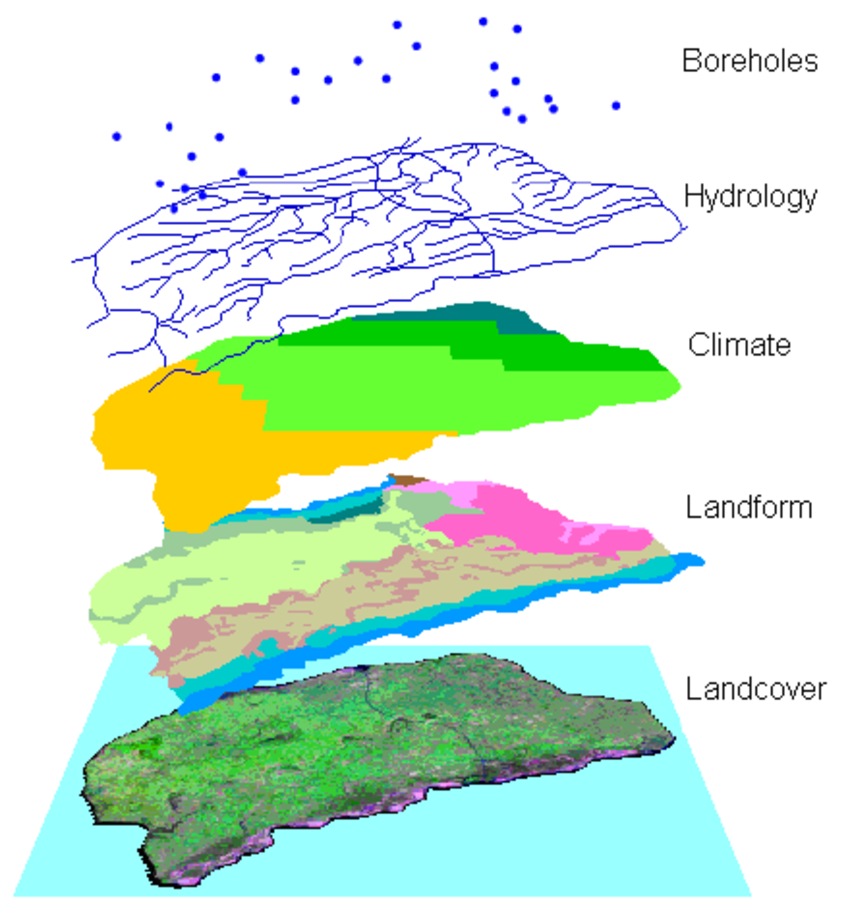
Physical geography focuses upon the character of, and processes shaping, the land-surface of the Earth and its envelope, emphasizes the spatial variations that occur and the temporal changes necessary to understand the contemporary environments of the Earth. Its purpose is to understand how the Earth's physical environment is the basis for.

Aspect (geography) Top 8 Facts YouTube
Physical geography is the spatial study of natural phenomena that make up the environment, such as rivers, mountains, landforms, weather, climate, soils, plants, and any other physical aspects of the earth's surface. Physical geography focuses on geography as a form of earth science.
The Five Themes of Geography WorldAtlas
At its core, geography is the study of the Earth's features, the processes that shape them, and the interrelationships between people and their environments. It's a discipline that bridges the gap between the physical and social science s. Geography can be broadly categorized into two main branches: 1. Physical Geography.

Geography 7 Lab Assignments
A slope which falls down to a deep valley on its western side and a shallower one on its eastern side has a westerly aspect or is a west-facing slope. The term can also be used to describe the shape or alignment of a coastline. Here, the aspect is the direction which the coastline is facing towards the sea. For example, a coastline with sea to.
What is Geographic Information System (GIS) Aspectum
Therefore, temperatures are higher in southern England than in the north of Scotland, mainly due to latitude. Latitude also affects rainfall. Places near the equator receive more precipitation (rain) due to low-pressure zones, which result in warm, moist air rising and condensing leading to convection rainfall.

Mr. E's World Geography Page World Geography 2017 Chapter 1 Physical Geography Looking at
Aspect (geography) explained. In physical geography and physical geology, aspect (also known as exposure) [1] is the compass direction or azimuth that a terrain surface faces. [2] For example, a slope landform on the eastern edge of the Rockies toward the Great Plains is described as having an easterly aspect. A slope which falls down to a deep.

Terrain Slope/Aspect Display And Analysis
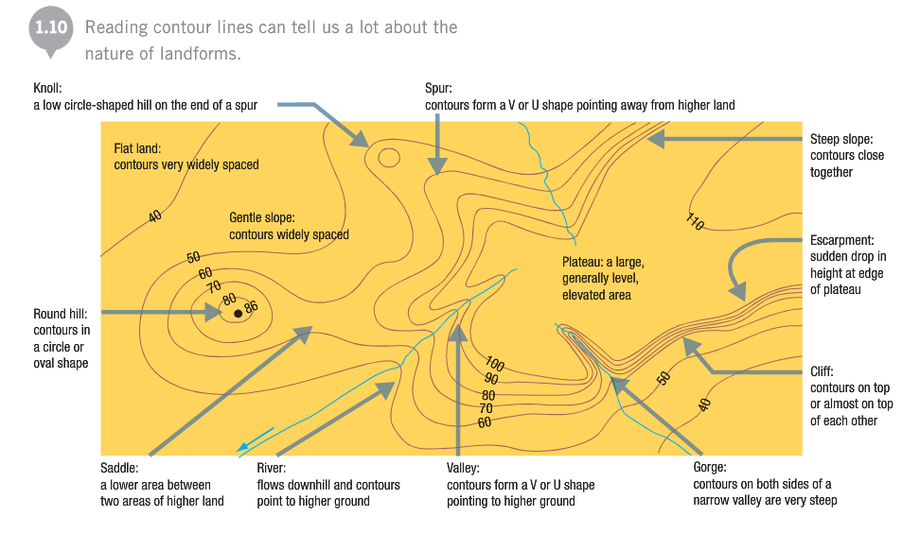
Watch 'Contours, gradient, relief and aspect' (3:20). Topographic maps allow geographers to identify landscape, gradient of a slope, relief and aspect. Stage 4 - Stage 5 - Geographical skills and tools - how cartographers create topographic maps using points of reference on the land.

Aspect of Slope explained mapreading contours contourlines maps YouTube
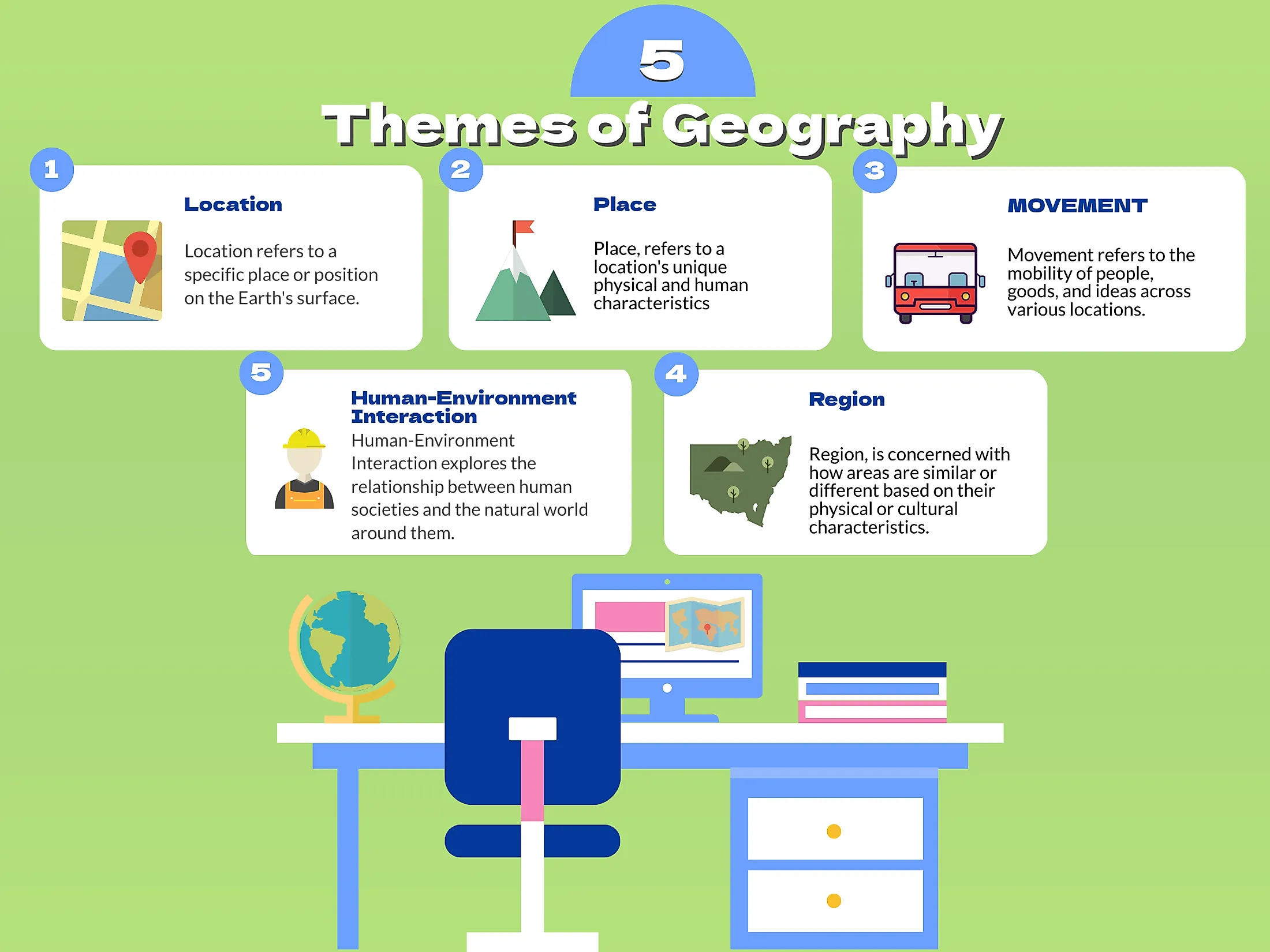
A geographer is a scientist who studies geography. Geographers have identified six essential elements of geography. The World in Spatial Terms. Places and Regions. Physical Systems. Human Systems.
GeoSkills Relief Year 8 Geography
About: Aspect (geography) In physical geography and physical geology, aspect (also known as exposure) is the compass direction or azimuth that a terrain surface faces. For example, a slope landform on the eastern edge of the Rockies toward the Great Plains is described as having an easterly aspect. A slope which falls down to a deep valley on.

Terrain Slope/Aspect Display And Analysis
The concept of an aspect map is simple to understand. Aspect values indicate the directions the physical slopes face. We can classify aspect directions based on the slope angle with a descriptive direction. An output aspect raster will typically result in several slope direction classes. Here is an example of an aspect map from the south point.

Aspect Maps How Do You Find Out the Aspect of a Slope? GIS Geography
In physical geography and physical geology, aspect (also known as exposure) [1] is the compass direction or azimuth that a terrain surface faces. [2] For example, a slope landform on the eastern edge of the Rockies toward the Great Plains is described as having an easterly aspect. A slope which falls down to a deep valley on its western side.