
Explain the Difference Between Gross and Net Primary Productivity
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.

Primary production graphics Eco fashion, Fashion encyclopedia, Primary
Primary production is the most basic building block for energy and the basis for food webs in all environments and ecosystems. In the ocean, autotrophs which are responsible for primary production consist of phytoplankton, marine plants, and macroalgae since they all perform photosynthesis. All photoautotrophs capture solar energy by utilizing.
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记5.3.5 Net Primary Production翰林国际教育
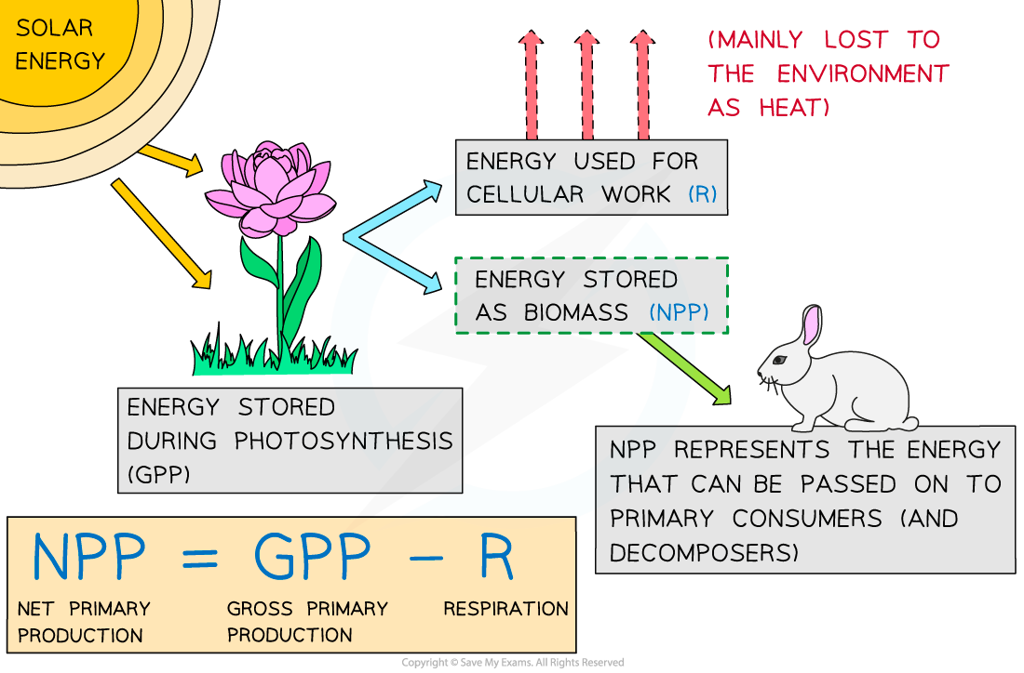
The general term " Production" is the creation of new organic matter. When a crop of wheat grows, new organic matter is created by the process of photosynthesis, which converts light energy into energy stored in chemical bonds within plant tissue. This energy fuels the metabolic machinery of the plant.
PPT Chapter 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID256818
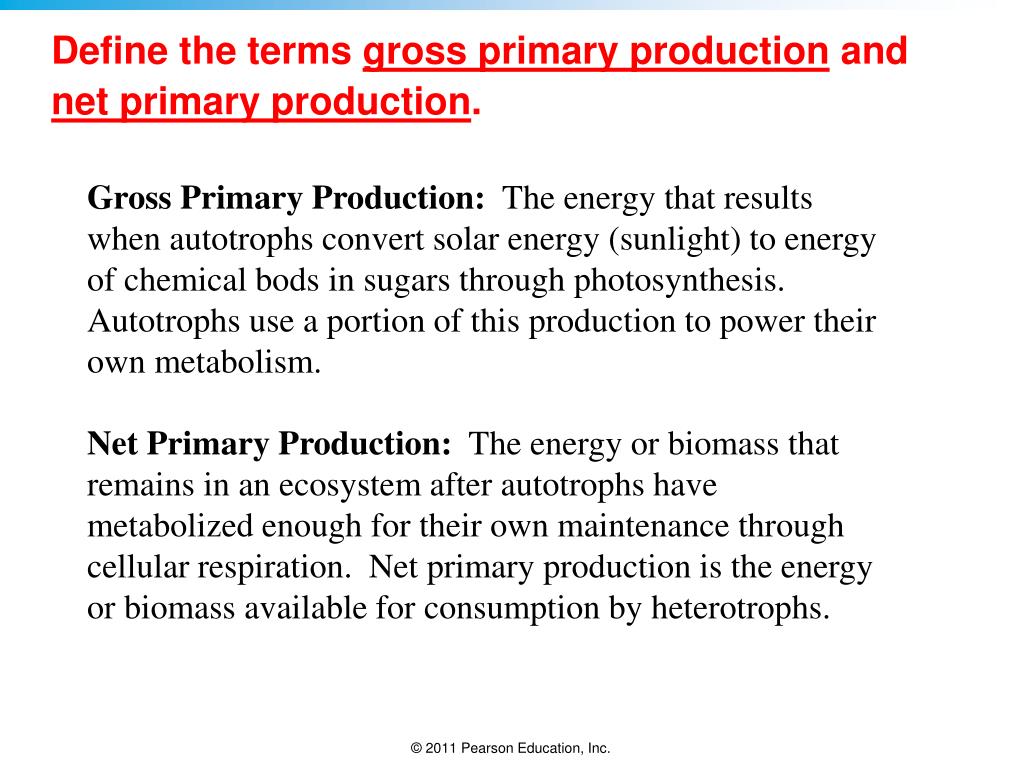
Gross primary production (GPP) is the total amount of carbon dioxide "fixed" by land plants per unit time through the photosynthetic reduction of CO 2 into organic compounds.
the production process Nageng primary school
Disadvantages of Relying on Primary Products. Prices are often volatile due to inelastic demand. e.g if there is a 'good harvest', supply will increase and there will be a fall in the price of primary products. However, because demand is inelastic, this would lead to a fall in revenue. The volatile price of coffee - can make planning.
PPT Ecosystems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1633779
7.1: Primary Production. Primary production is the creation of new organic matter from inorganic substrates, and it is this organic matter that serves as the base of the food web for most marine consumers. Primary production generally refers to the process of photosynthesis, or the utilization of light energy to produce chemical fuels that is.

Primary Production YouTube
primary productivity, in ecology, the rate at which energy is converted to organic substances by photosynthetic producers (photoautotrophs), which obtain energy and nutrients by harnessing sunlight, and chemosynthetic producers (chemoautotrophs), which obtain chemical energy through oxidation. Nearly all of Earth's primary productivity is.
Primary productivity Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Primary production is the production of chemical energy in organic compounds by living organisms. The main source of this energy is sunlight but a minute fraction of primary production is driven by lithotrophic organisms using the chemical energy of inorganic molecules. Regardless of its source, this energy is used to synthesize complex organic.
PPT Ecosystem Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2742411
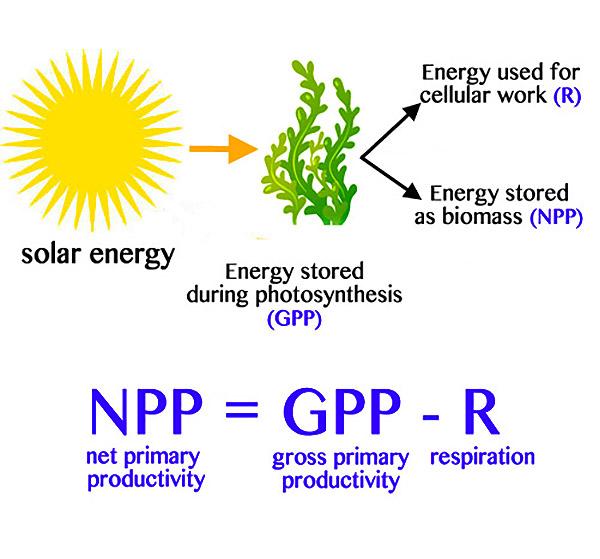
Primary productivity refers to the rate at which autotrophs convert carbon dioxide into organic material during photosynthesis, and the total primary production within an ecosystem is the gross primary production, or GPP. However, autotrophs spend some of their energy during cellular respiration, leaving less for consumption by heterotrophs.

A primary producer is an individual, partnership, trust or company operating a primary
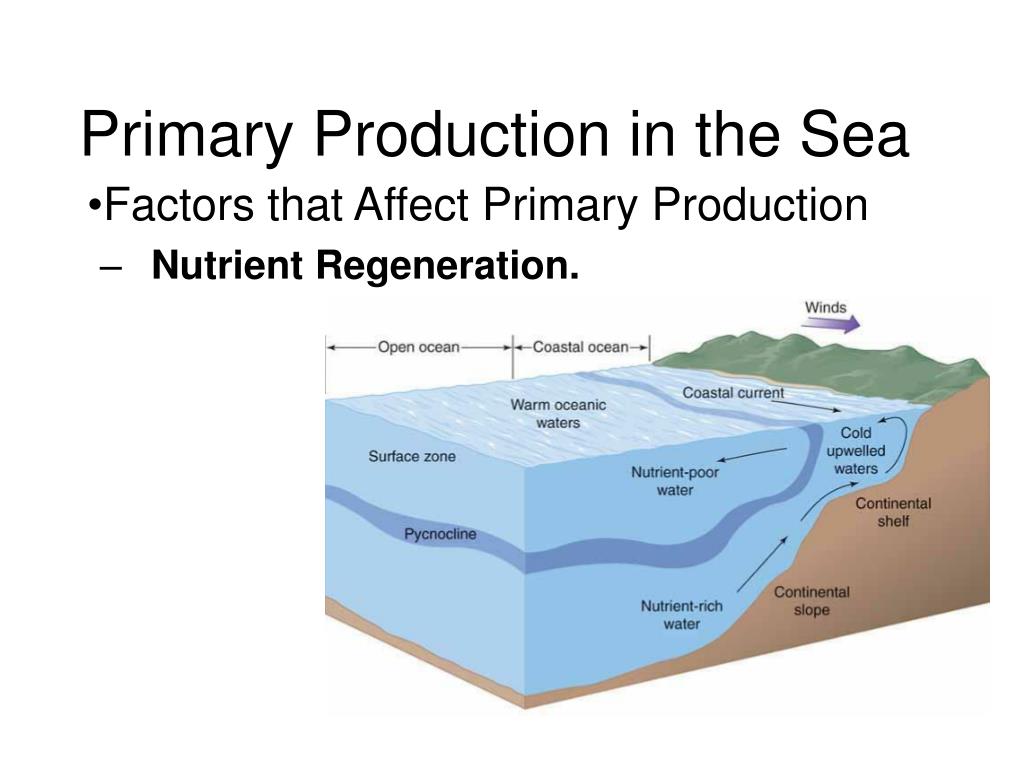
Ocean productivity largely refers to the production of organic matter by " phytoplankton ," plants suspended in the ocean, most of which are single-celled. Phytoplankton are " photoautotrophs.

PPT Primary Production PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1308879
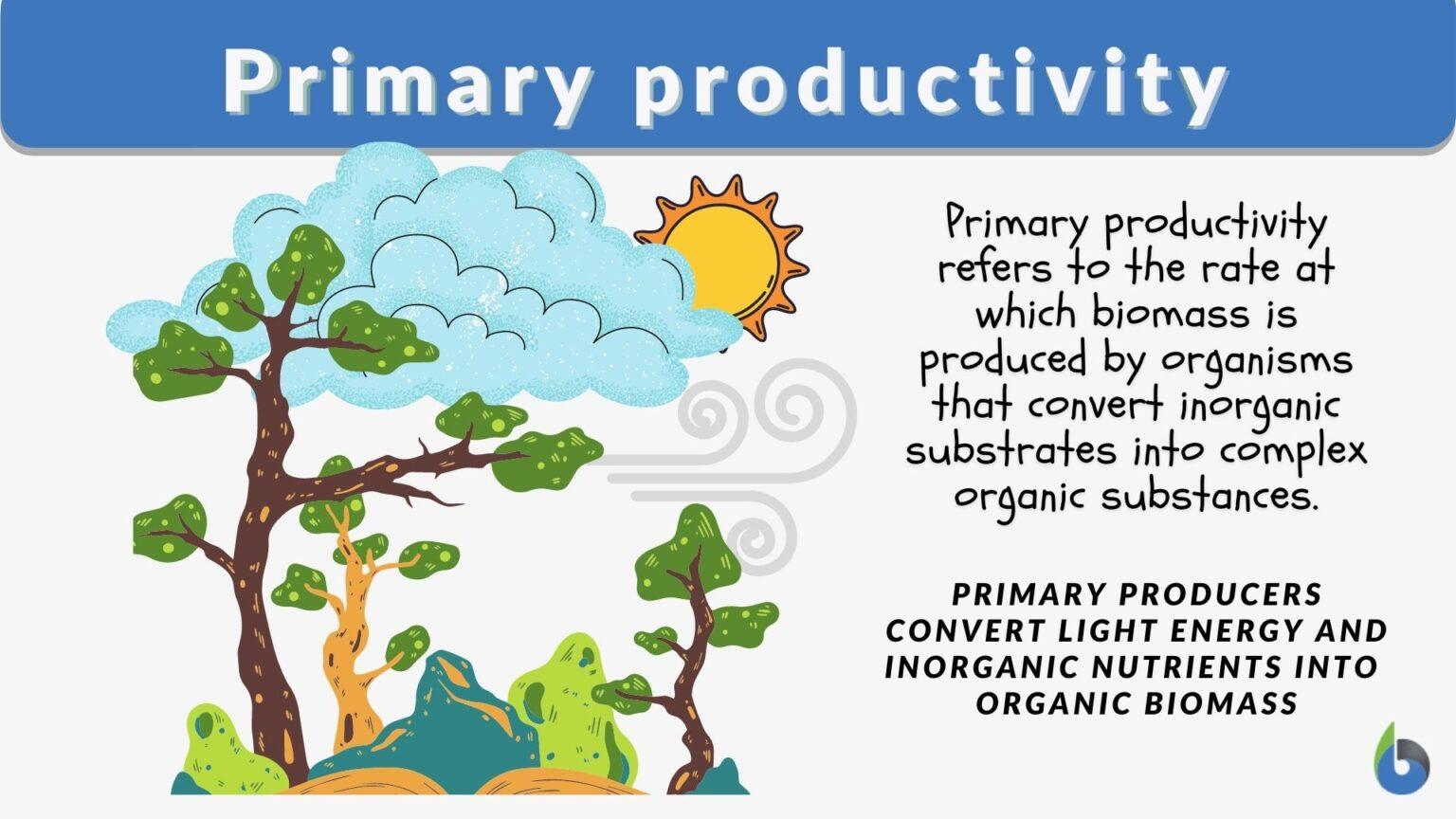
Primary productivity is the rate at which biomass is produced by organisms that convert inorganic substrates into complex organic substances. Primary production typically occurs through photosynthesis; when green plants convert solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water to glucose, and eventually to plant tissue.
Net primary productivity Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Net primary production ( NPP) refers to the amount of energy available to herbivores in the plant's biomass after plant respiratory losses. Of total energy trapped in glucose during photosynthesis, 90% of this energy will be released from glucose to create ATP for the plant. The plant uses most of its glucose to fuel active cellular processes.

PPT Primary Productivity PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5338600
Production is the process in which various inputs such as land, labor, and capital are used to produce the outputs in the form of products or services. For example, you own a firm and by utilizing factors of production, you produce your products. This mechanism is known as production.
PPT Food Chains and Food Webs PowerPoint Presentation ID294430
Primary production is typically measured as the amount of biomass produced per unit area, where biomass is the mass of plant material. The term, primary productivity, refers to primary production over time, or the rate of primary production.If gaseous exchange methods are used to measure primary productivity, the time period is a day or an hour and the units are grams of oxygen evolved or.

Energy in ecosystem new
Primary producers (usually plants and other photosynthesizers) are the gateway for energy to enter food webs. Productivity is the rate at which energy is added to the bodies of a group of organisms (such as primary producers) in the form of biomass. Gross productivity is the overall rate of energy capture. Net productivity is lower, adjusted.
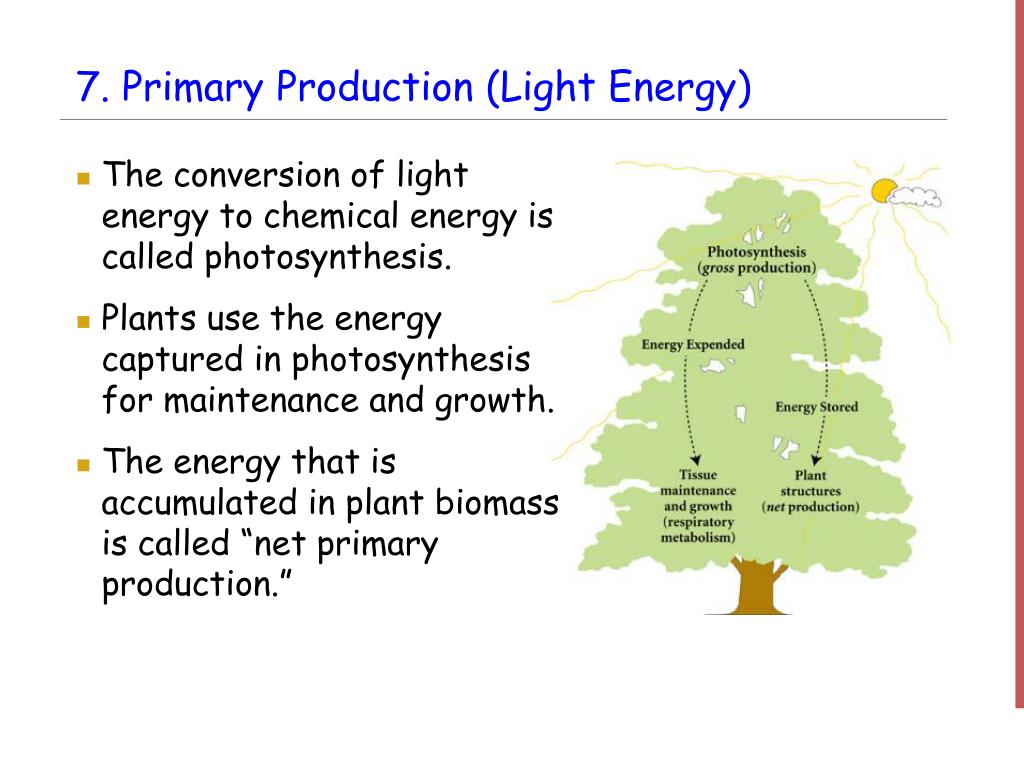
PPT Interdependence of Life Ecosystems PowerPoint Presentation ID371924
Primary productivity is the rate at which energy is converted to organic substances in a region or ecosystem. Energy is converted through autotrophic (self-feeding) organisms, converting solar or chemical energy into biomass. Basically, primary production is generation of food by making organic matter from inorganic matter.
- Paris Café De La Danse
- 23 Commercial Road Port Noarlunga South
- Stun Baton Sons Of The Forest
- Dr Daniel Tan Associates Reviews
- Tv Shows With Richard Rankin
- Hotel Indigo Dallas Downtown Dallas Tx
- Cleaning Out The Closet Lyrics
- Royal Children S Hospital Good Friday Appeal
- Pet Paw Print Kit Australia
- Hotel Near Zurich Hb Train Station