
Brain Tumors in Pets Never Ignore These Symptoms
Radiation therapy has been used successfully as the primary treatment of meningiomas in cases where surgery is not a possibility. Most dogs are treated with radiation therapy for approximately four weeks, five days a week. The radiation therapy will be tailored to your dog's tumor location and size to ensure maximum success in shrinking the.

Canine brain tumours a model for the human disease? Hicks 2017 Veterinary and Comparative
Although brain tumors are the most common cause of new-onset neurological symptoms in older dogs, it is important to keep an open mind about differential diagnoses in these patients. Some people, pet owners, and veterinarians alike will assume that simply because a dog is senior, any new onset neurological symptoms must be due to a brain tumor.

A Pet Owners Guide to Brain Cancer in Dogs Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Causes of Brain Tumors in Dogs. There are no known direct causes of brain tumors in dogs. Research suggests that a combination of factors, such as diet, surrounding environment, genetics, and immune system health, may be involved. Brain tumors can occur at any age but typically happen in dogs over the age of 5.

Canine Brain Tumors Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
An abnormal movement in a limb, for example. A brain tumour is just one possible cause for seizures. There might be signs specific to tumour location. Reduced sensation, weakness, loss of balance or staggering, visual impairment or blindness, and changes in sense of smell can happen. These signs may be subtle or severe.

The Most Common Symptoms of Brain Tumors in Dogs
The diagnosis of a brain tumor in dogs typically starts with a thorough physical examination by your veterinarian (including a careful neurologic examination to look at the pupils, the response to light, the reflexes in the limbs, etc.). Additional tests to diagnose a brain tumor include: Emergency treatment for a brain tumor is often necessary.

Signs the Brain Tumor in Your Dog is Progressing » Scary Symptoms
By far, the most common type of brain tumor in both dogs are meningiomas, which account for approximately 40-45 percent of cases. These may occur at any age, but most dogs affected are greater than five years of age. Dogs can also develop pituitary gland tumors. The pituitary gland sits at the base of the brain and is associated with the.

What Are The Symptoms Of A Brain Tumor In A Dog
A dog brain tumor is a serious and often heartbreaking diagnosis for pet owners. The progression timeline of a dog brain tumor can vary greatly depending on the type of tumor, its location, and how aggressively it is treated. Understanding the stages of progression can help pet owners make informed decisions about their dog's care and quality.

10 Common Brain Tumor Symptoms in Dogs Southeast Veterinary Neurology
There are three ways of treating brain tumors in dogs: Neurosurgery, performed by an experienced, board-certified veterinary surgeon. Radiation therapy, administered alone or in combination with other treatments. Chemotherapy medication, which may shrink the tumor and improve clinical signs. Steroids may be used to decrease fluid buildup, or to.

Brain Tumor in Dogs Prognosis, Survival, Symptoms, and Treatment
Here are several other possible symptoms of brain tumors in dogs: Blindness or impaired vision. Abnormal eye movement. Head tilting or rotating. Circling. Unusual aggression or abnormal behavior.

Brain Tumors In Dogs Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
A tumor is an uncontrolled growth of cells within tissue. These abnormal cells create masses that destroy healthy tissue. Therefore, a tumor in the brain will cause brain damage, resulting in serious neurological symptoms. Types of Brain Tumors in Dogs. There are two main types of brain tumors in dogs: primary and secondary. Primary

How To Tell If Your Dog Has Brain Tumor How Would I Know If My Dog Has A Brain Tumour Vet Help
Brain tumors may be primary, arising from the cells of the brain and its lining (figure 2), or secondary, arising elsewhere and spreading to the brain. Primary brain tumors seen in dogs and cats include meningioma, glioma, choroid plexus papilloma, pituitary adenoma or adenocarcinoma, and others. Meningioma - This is the most common primary.

Dog Brain Tumor When to Euthanize? (Advice from Vets) Family Life Share
A brain tumor is a serious condition caused by improper cell division in tissues associated with the brain. These cells are unable to receive the "stop growing" signal and continue to divide, forming masses that can replace or damage healthy brain tissue. Brain damage can cause abnormal behavior, weakness or lethargy, and difficulty moving.

Brain Tumor in Dogs Prognosis, Survival, Symptoms, and Treatment
Seizures - This is the most common initial sign of a brain tumor. Symptoms can include collapsing, jerking, stiffening, twitching, loss of consciousness, drooling, chomping, tongue chewing, or foaming at the mouth. Dogs can fall to the side and make paddling motions with their legs.
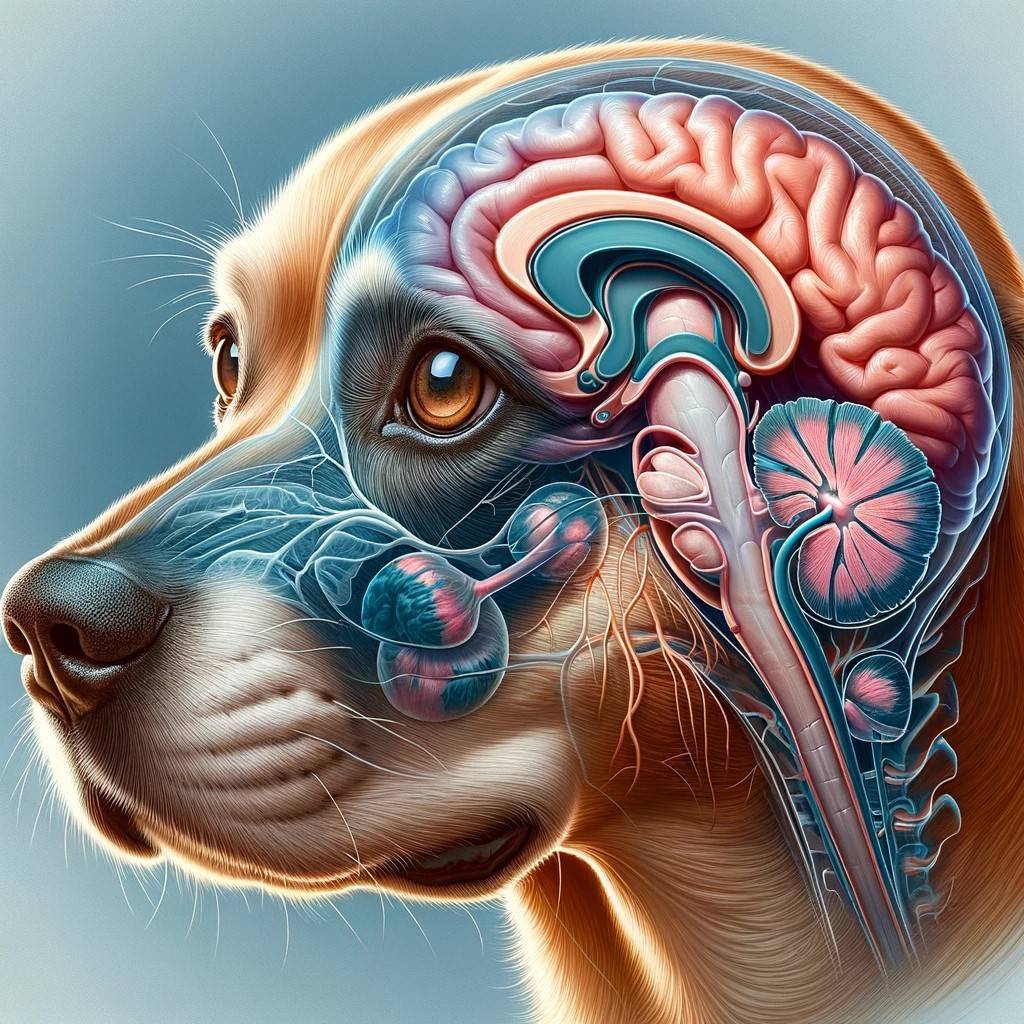
Symptoms Of Brain Tumor In Dogs Red Flags Every Owner Should Know
Some of the most common symptoms of brain tumors in dogs include: Seizures. Head tilt. Changes in behavior such as aggression, confusion, etc. Unsteady gait or wobbly movement. Changes in vision. Nystagmus (rapid movement of the eyes causing dizziness) Hypersensitivity in the neck. Head pressing.

Is Brain Tumor In Dogs Curable? Brain tumor, Tumor, Dogs
Symptoms- Many dogs with brain tumors show vague signs like changes in behavior. These symptoms are so negligible, that owners and vets tend to overlook them till signs of brain dysfunction are well developed. These include subtle behavior alterations, that usually develop over months and years. Like humans, dogs may also develop severe.

Brain Tumor in Dogs Prognosis, Survival, Symptoms, and Treatment
Brain tumor symptoms in dogs can vary widely, depending on the tumor's size, location, and rate of growth. Common signs may include: Behavioral changes: Dogs may display uncharacteristic aggression, confusion, or decreased interaction. Loss of coordination: This can manifest as stumbling, circling, or difficulty walking.
- How Much Is A 1988 50 Cent Coin Worth
- Where Does Air Nz Fly To
- Basilica Di Santa Maria In Trastevere
- What Colour Is Irish Green
- 5 Letter Words Ending In Uth
- Holden 202 Performance Engine For Sale
- Leonardo Da Vinci Interactive Museum
- Where To Watch Good Doctor Season 6
- Friendship Necklaces For 3 Friends
- Diary Of A Wimpy Kid Full Movie