Transformer Definition, Types, Working Principle, Equations & Examples (2024)
Electric Motors, Generators, and Transformers. As we learned previously, a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field experiences a force—recall F = I ℓ B sin θ F = I ℓ B sin θ. Electric motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, are the most common application of magnetic force on current-carrying wires.Motors consist of loops of wire in a magnetic field.

Electrical and Electronics Engineering How a Transformer Works
transformer, device that transfers electric energy from one alternating-current circuit to one or more other circuits, either increasing (stepping up) or reducing (stepping down) the voltage.Transformers are employed for widely varying purposes; e.g., to reduce the voltage of conventional power circuits to operate low-voltage devices, such as doorbells and toy electric trains, and to raise the.
How Transformers Work Homemade Circuit Projects
Figure 15.7.2 15.7. 2: Transformers are used to step down the high voltages in transmission lines to the 110 to 220 V used in homes. (credit: modification of work by "Fortyseven"/Flickr) As Figure 15.7.3 15.7. 3 illustrates, a transformer basically consists of two separated coils, or windings, wrapped around a soft iron core.

step up transformer working function animation video,ac transformer working function, YouTube
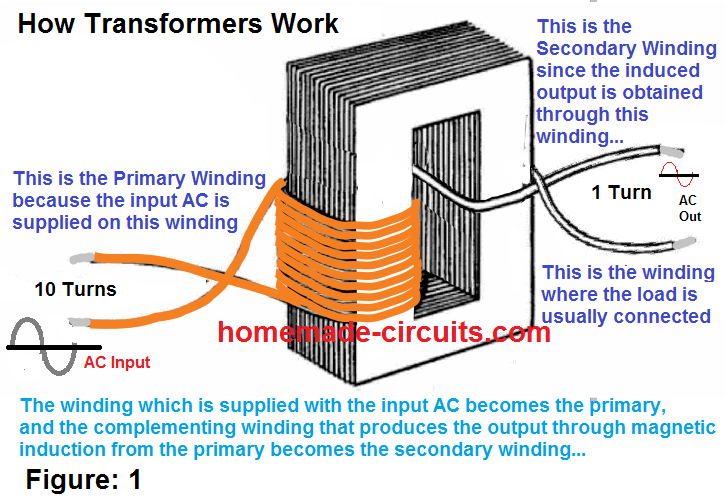
Working Principle of Transformer. The working principle of a transformer is very simple.Mutual induction between two or more windings (also known as coils) allows for electrical energy to be transferred between circuits. This principle is explained in further detail below. Transformer Theory. Say you have one winding (also known as a coil) which is supplied by an alternating electrical source.
Step Up Transformer Construction & Working Principles Linquip
How does a transformer work? A transformer is based on a very simple fact about electricity: when a fluctuating electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field (an invisible pattern of magnetism) or "magnetic flux" all around it.The strength of the magnetism (which has the rather technical name of magnetic flux density) is directly related to the size of the electric current.

How Transformers Work
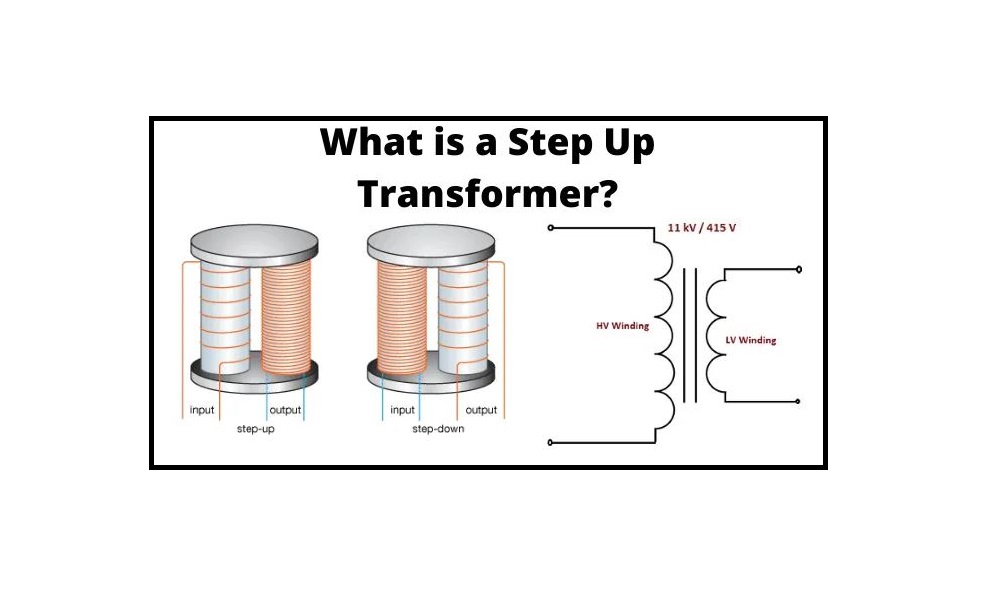
Transformers step up (increase) or step down (decrease) AC voltage using the principle of electromagnetic induction - mutual induction. A changing current in the primary coil induces an e.m.f in the secondary. Since the e.m.f generated depends on the number of turns, the voltage induced in the secondary can be changed - stepped up or down - by.

TRANSFORMERS (PHYSICS) HOW DO THEY WORK YouTube
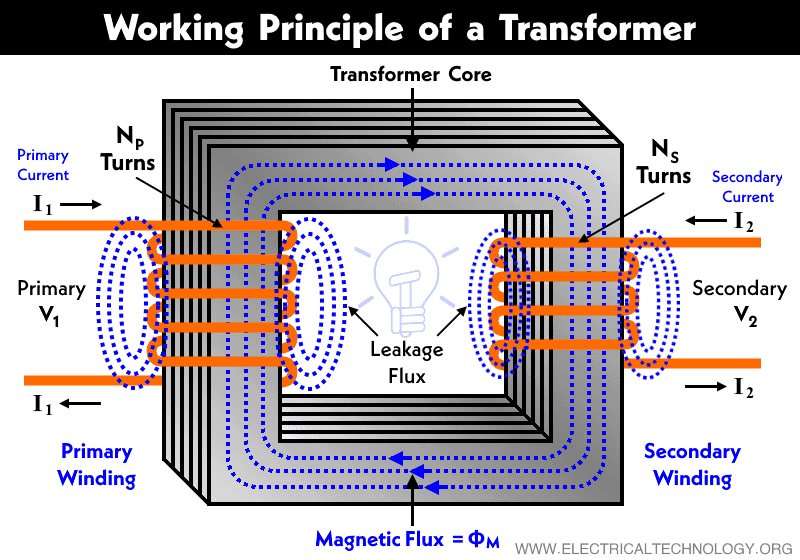
The type of transformer considered in this text—see Figure 23.27—is based on Faraday's law of induction and is very similar in construction to the apparatus Faraday used to demonstrate magnetic fields could cause currents. The two coils are called the primary and secondary coils.In normal use, the input voltage is placed on the primary, and the secondary produces the transformed output.

Transformer Definition, Types, Working Principle, Equations & Examples
Transformers use electromagnetic induction to change the voltage of alternating currents. The voltage and current changes can be calculated, as the power transfer is constant. Part of Physics.

IGCSE Physics Transformers How and Why? YouTube
How does a transformer work. In this video we'll be looking at how a transformer works covering the basics with transformer working animations and explanatio.

What is the Working Principle of a Transformer?
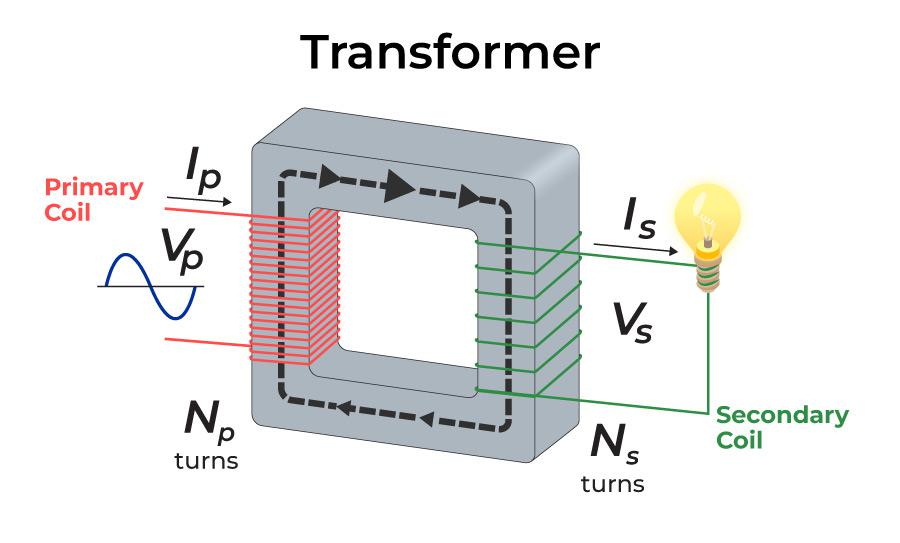
The iron core of a transformer is normally a complete ring with two coils wound on it. One is connected to a source of electrical power and is called the primary coil; the other supplies the power to a load and is called the secondary coil. The magnetisation due to the current in the primary coil runs all the way round the ring.
What is an Ideal Transformer? Circuit and Phasor Diagram
Transformers do what their name implies—they transform voltages from one value to another (The term voltage is used rather than emf, because transformers have internal resistance). For example, many cell phones, laptops, video games, and power tools and small appliances have a transformer built into their plug-in unit (like that in Figure 1) that changes 120 V or 240 V AC into whatever.

Transformer Definition, Types, Working Principle, Diagram
Figure 23.5.1: A transformer converts a primary alternating voltage, ∆ Vp, to a secondary alternating voltage, ∆ Vs. The magnetic flux produced in one coil is transmitted by an iron core to the secondary coil, where a different voltage is induced, depending on the ratio of the number of windings in each coil. The transformer has two coils.

How Do Transformers Work? YouTube
A transformer is made up of: A primary coil. A secondary coil. An iron core. The primary and secondary coils are wound around the soft iron core. The soft iron core is necessary because it focuses and directs the magnetic field from the primary to the secondary coil. Soft iron is used because it can easily be magnetised and demagnetised.

How do transformers work? Algebrabased physics YouTube
Transformers are manufactured to be step up or step down transformers and these are used to increase or decrease the voltage simply by using a different number of turns within the coil on the secondary side. In a step up transformer, the voltage is increased in the secondary coil and this will mean that the current will decrease, but don't.

iGCSE Physics Transformers YouTube
How transformers work 🎁 Skillshare: https://skl.sh/theengineeringmindset05221 The first 1,000 people to use the link or my code theengineeringmindset will g.

How does a transformer work? YouTube
A transformer makes use of Faraday's law and the ferromagnetic properties of an iron core to efficiently raise or lower AC voltages. It of course cannot increase power so that if the voltage is raised, the current is proportionally lowered and vice versa. Show. Calculation. Reflected Load in a Transformer.
- 5 Camilla Court New Port
- Flights From Sydney To Proserpine
- Type Of Lily Crossword Clue
- Alison Moyet All Cried Out
- Skin Rash From Band Aid
- The Joker And The Thief Terrigal
- Where Is Fisher And Paykel Washing Machines Made
- Wilson Parking 123 Albert Street
- Lamborghini For Sale Real Car
- Melbourne Royal Dog Show 2023