
a d Gas chromatography with flame ionization detector (GCFID)... Download Scientific Diagram
Gas chromatography (GC) is used to separate and detect small molecular weight compounds in the gas phase. The sample is either a gas or a liquid that is vaporized in the injection port. Typically, the compounds analyzed are less than 1,000 Da, because it is difficult to vaporize larger compounds. GC is popular for environmental monitoring and.

Flame Ionization Detector (FID) Principle Inst Tools
Detectors Flame Ionization Detector (FID) FID is the standard workhorse detector for the GC. It is specific, destructive, has a wide linear range and a limit of detection of 5 pg carbon/second. Production of ions in a flame result in a current that can be measured. A make-up gas may be required to maintain an optimum flow - capillary columns.

Agilent, HP 6890 gas chromatograph with flame ionization detector and... Download Scientific
As the flame ionization detector (FID) approaches its 60th anniversary in 2017, this installment examines the crucial role that it has played and continues to play for all types of gas chromatography. Without the FID, the early development of gas chromatography (GC) would have proceeded more slowly especially in the petroleum industry and related hydrocarbon application areas.

Write a Note on Flame Ionization Detector. Chromatography Analytical Chemistry YouTube
Flame ionization detection (FID) is the most commonly used gas chromatography (GC) detection method. Flame ionization detectors respond to a wide assortment of hydrocarbons, have a large dynamic range, are relatively simple to operate and are considered highly reliable. Unfortunately, GC users are often led into a false sense of security as a.

12.4 Gas Chromatography Chemistry LibreTexts
One of the earliest gas chromatography detectors takes advantage of the mobile phase's thermal conductivity. As the mobile phase exits the column it passes over a tungsten-rhenium wire filament (see Figure 12.4.10 .. This is the basis of the popular flame ionization detector, a schematic diagram of which is shown in Figure 12.4.11 . Figure.
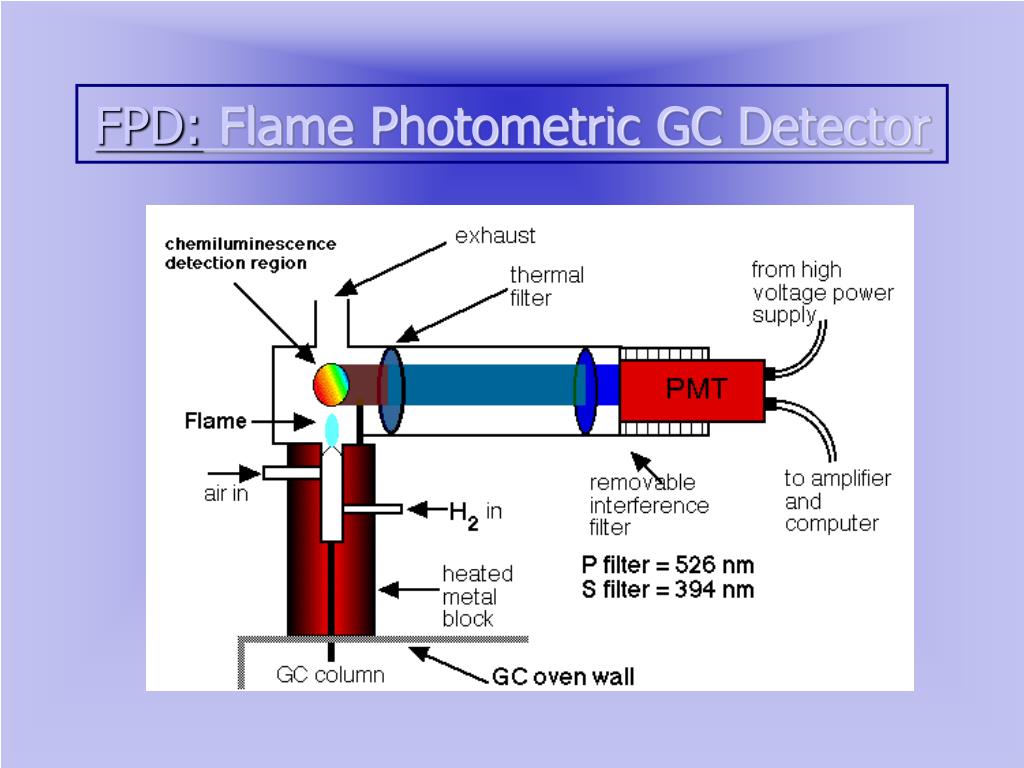
PPT Gas chromatography PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5672764
A Flame ionization detector (FID) consists of a hydrogen (H 2 )/air flame and a collector plate. The effluent from the GC column passes through the flame, which breaks down organic molecules and produces ions. The ions are collected on a biased electrode and produce an electrical signal. The FID is extremely sensitive with a large dynamic range.

Bench Top Lab Analyzer Machine Portable Gas Chromatograph with Flame Ionization Detector (FID
A number of detectors are used in gas chromatography. The most common are the flame ionization detector (FID) and the thermal conductivity detector (TCD). Both are sensitive to a wide range of components, and both work over a wide range of concentrations. While TCDs are essentially universal and can be used to detect any component other than.

China Flame Ionization Detector Fid for Gas Chromatograph Gc7860 China Gas Chromatograph, Gas
Application error: a client-side exception has occurred (see the browser console for more information). Flame ionization detection (FID) is the most commonly used gas chromatography (GC) detection method. Flame ionization detectors respond to a wide assortment of hydrocarbons, have a large dynamic range, are.

China Flame Ionization Detector Fid for Gas Chromatograph Gc7860 China Gas Chromatograph, Gas
The flame ionization detector (FID) is the most widely used detector for gas chromatography because of its reliability, versatility, and ease of use. It responds to virtually any organic compound while generating little or no signal for common carrier gases. The auto-ranging FID used on Agilent Intuvo 9000, 8890, 8860, and 7890 GC systems.

Flame Ionization Detector SkillLync YouTube
An FID, or Flame Ionization Detector, is the most common detector paired with gas chromatography instruments for analytical applications. But how does and FID work? An FID uses a flame to ionize organic compounds containing carbon. Following separation of the sample in the GC column, each analyte passes through a flame, fueled by hydrogen and.

GC Analysis Part II. The Flame Ionization Detector (FID) Phytochemia
Flame ionization detectors (FID) are the most generally applicable and most widely used detectors. In a FID, the sample is directed at an air-hydrogen flame after exiting the column.. REview of Photoionization Detection in Gas Chromatography: The first Decade. Journal of CHromatographic Science , Vol 23. November 1985. 488-492.
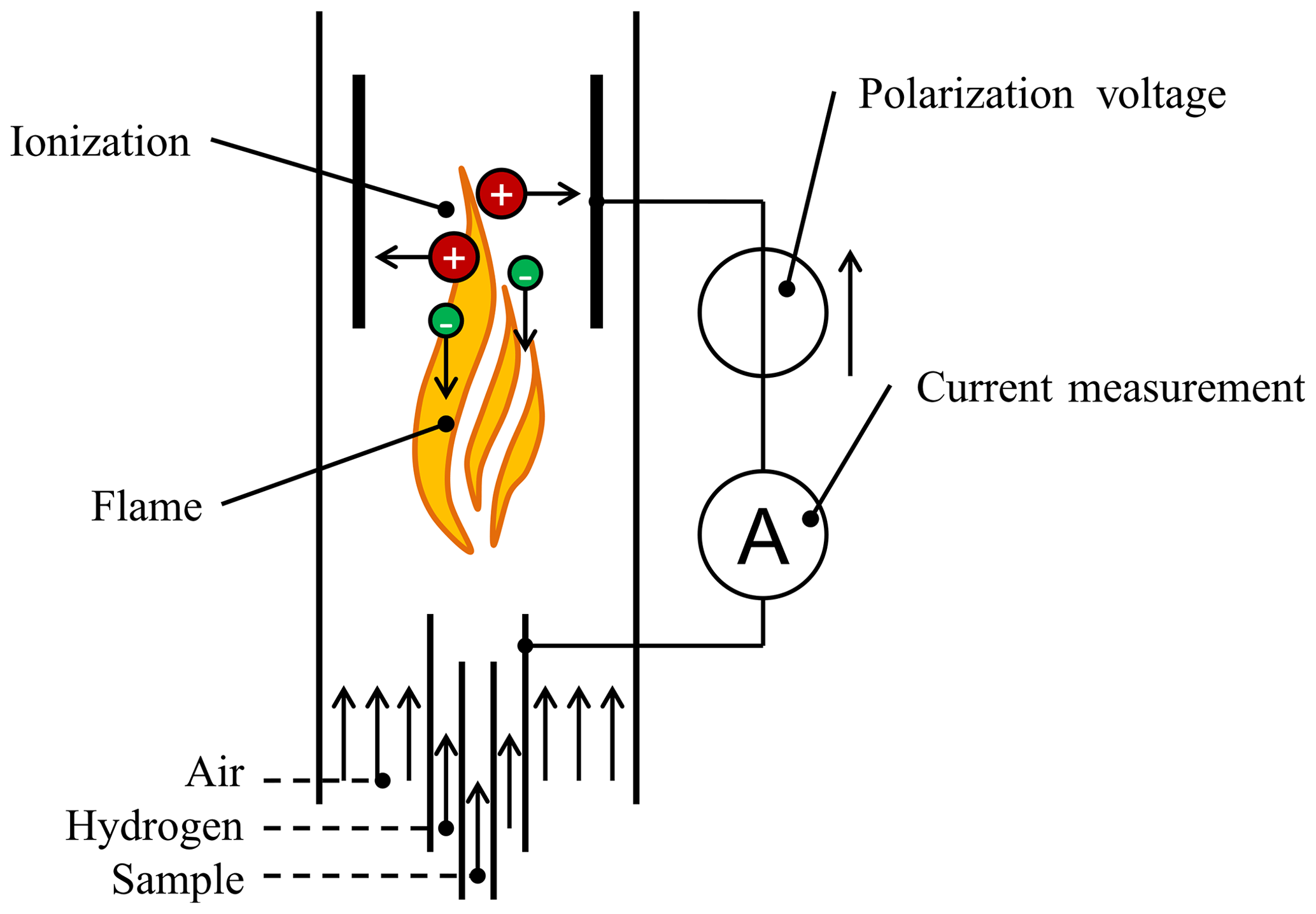
JSSS An autonomous flame ionization detector for emission monitoring
Gas Chromatography Detectors Detector Description Linear Dynamic Range Destructive Analytes Flame Ionization Detector The FID is the most commonly used general-purpose GC detector. As the sample exits the column, it is burned in a hydrogen/air flame and ionized particles are measured as an electrical current. >107 (±10%) Yes Most organic compounds

Gas Chromatography Flame Ionization Detector or GCFID Gas
Instrumentation, namely gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has been useful in the quantification of volatile compounds and barrel extractives, respectively. Until recently, instrumentation has been limited by its detection capabilities. Many taint compounds, such as geosmin, 2.
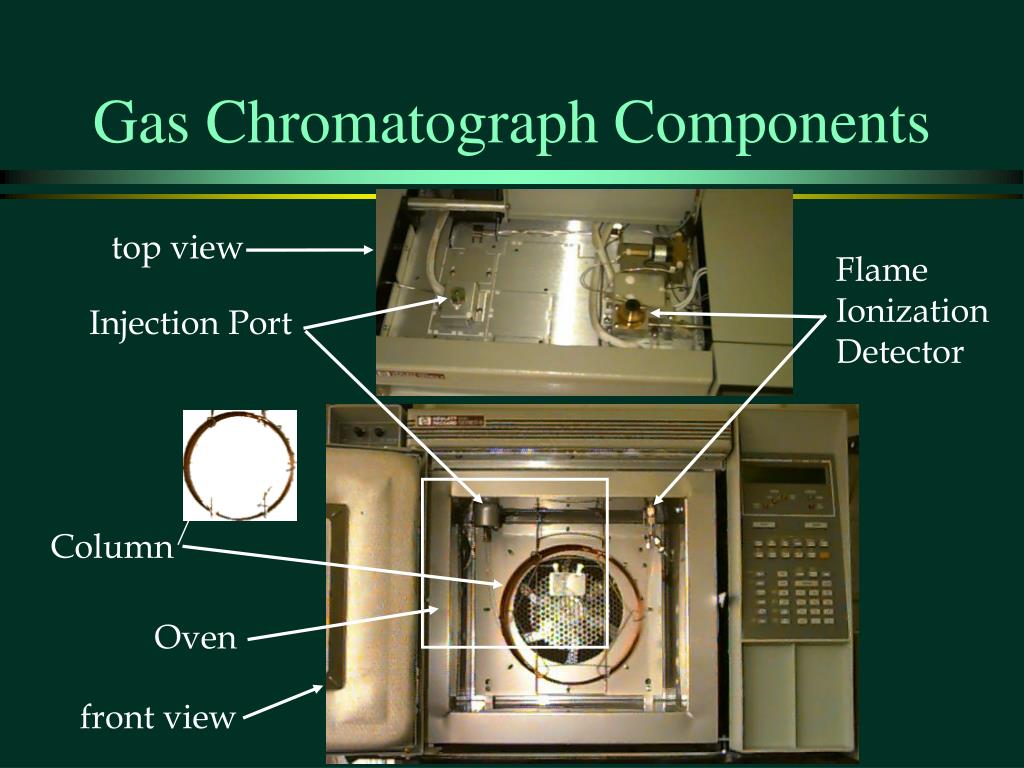
PPT Gas Chromatography PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID787942
Set oven temp to Ambient (35C) Turn off column flow. Shut off all detector gases. Turn off FID flame. Cool detector. Connect adapter to detector by inserting into FID as far as possible. Turn on one detector flow at a time allowing the gas to equilibrate in the flowmeter tubing before taking a measurement.

(a and b) Flame ionization detector spectra of gas chromatography at... Download Scientific
One of the earliest gas chromatography detectors takes advantage of the mobile phase's thermal conductivity. As the mobile phase exits the column it passes over a tungsten-rhenium wire filament (see Figure 27.2.6 ).. This is the basis of the popular flame ionization detector, a schematic diagram of which is shown in Figure 27.2.7 . Figure.

Gas chromatograph with flame ionization detector LUT University Research Infrastructure
Gas chromatography with flame ionization detection (GC-FID) is a widely used analytical technique that allows for the separation, identification, and quantification of volatile and semi-volatile compounds in a sample. Sample is injected into a heated inlet, vaporizing the sample at ca. 350 °C. The vaporized material is then pulled into the.
- L Frank Baum Oz Books
- Converse All Star Chuck Taylor All Star
- Charlotte Hornets Vs Brooklyn Nets Stats
- Towns That Start With V
- The Bold And The Beautiful Music
- Interesting Facts About The Three Sisters
- Ojo Bear In The Big Blue House
- Just For Today Alcoholics Anonymous
- Skyline Gtr For Sale Japan
- Hyams Beach Seaside Cottages Hyams Beach Nsw