
Earth Cross Section Diagram The Earth Images
A cross-section of the Earth, showing the sub-surface layers that are being mapped.
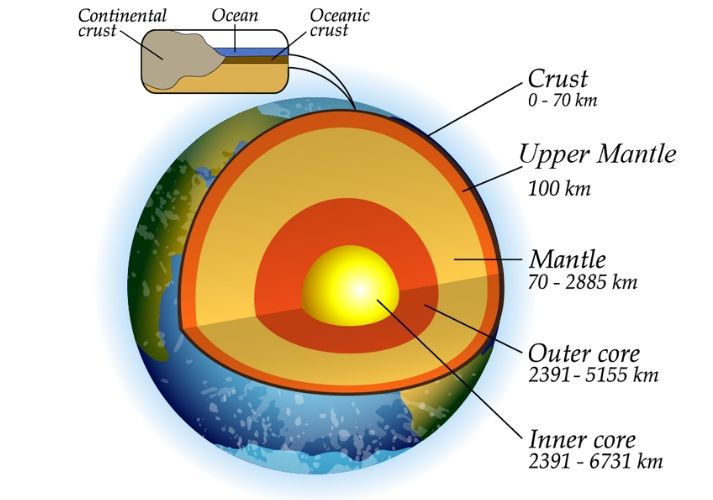
The Layers of the Earth Educational Resources K12 Learning, Earth Science, Science Lesson Plans
The mantle is roughly 2,900 km thick. In terms of volume, the mantle is the largest of earth's three chemical layers. Core:The final layer is the core, which is mostly iron and nickel. The core is about 3,500 km thick. Table 14.1.1 14.1. 1 summarizes the chemical layers of the earth.

Earth Cross Section Diagram The Earth Images
Diagram a cross section of the Earth's interior and describe each layer. Diagram the rock cycle; Define what a mineral is and describe the major mineral families that make up most rocks. Describe the origin and characteristics of sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. Create a diagram of intrusive igneous rock bodies.
Earth Tapestry, Earth Cross Section Showing the Inner Core Geology Science Themed Structure
The Cross section of the Earth is a visualization of the composition of the Earth in geological terms. The planet Earth is an immensely complicated and dynamic system, with many different physical and chemical properties. Most human experience of the Earth is limited to the surface however, with the deepest human endeavor made in 2012 to depths of 11 km in the Mariana's Trench.

Structure of the Earth, illustration Stock Image F025/0543 Science Photo Library
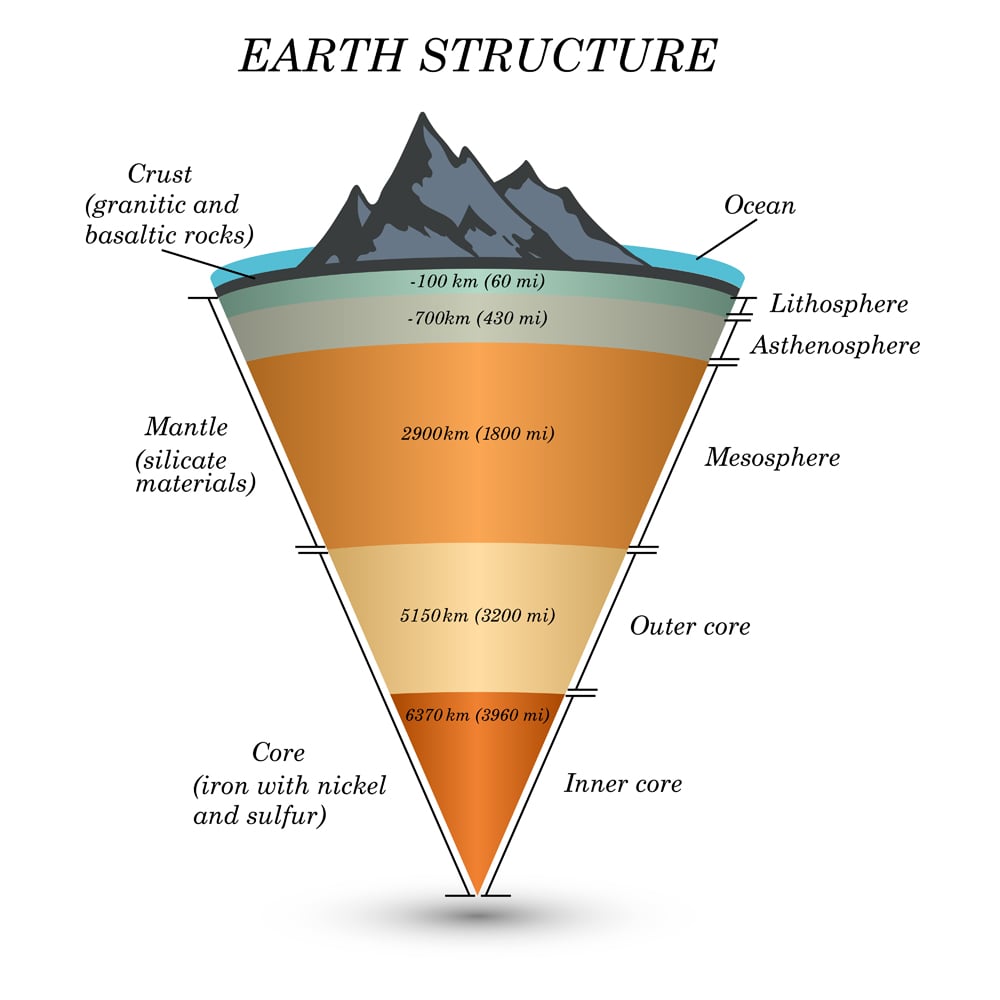
The outermost layer of the Earth is the crust. The crust is the thinest layer. There are two types of crust: oceanic and continental. Continental crust, varying in thickness from 20 to 200 kilometres, is not as dense as its oceanic counterpart.Primarily composed of granite, this crust is indestructible and significantly older than oceanic crust, with an age reaching up to 3.8 billion years.
Is Mount Everest Really The Tallest Mountain On Earth? » Science ABC
Figure 4.5: "Cross-section of Earth" (CC-BY 4.0; Chloe Branciforte and Cynthia Lampe, own work) This page titled 4.2: Activity 4A - The Structure of Internal Earth is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Chloe Branciforte & Emily Haddad ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative ) .
The Internal Structure of Earth(Geography) Forestry Bloq
A cross-section of the Earth. March 17th 2017. "In every outthrust headland, in every curving beach, in every grain of sand there is a story of the earth.". - Rachel Carson (American zoologist), 1907-1964. We now know that the Earth is many billions of years old, and that it has changed an unimaginably number of times over millennia.

Chartlet Cross Section Of The Earth by Carson Dellosa Science
The structure of the earth is divided into four major components: the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. Each layer has a unique chemical composition, physical state, and can impact life on Earth's surface. Movement in the mantle caused by variations in heat from the core, cause the plates to shift, which can cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
/cross-section-of-planet-earth-showing-the-inner-core-made-by-solid-iron-and-nickel-with-a-temperature-of-4500-celsius-188058517-572d7ab43df78c038eaeb09a.jpg)
The Earth's Crust Everything You Need to Know
Inner Core. Temperature: 5,000°C - 6,000°C State: Solid Composition: iron and nickel. The Earth's inner core is a huge metal ball, 2,500km wide. Made mainly of iron, the temperature of the ball is 5,000°C to 6,000°C - that's up to 6,000 times hotter than our atmosphere and scorching enough to make metal melt! The metal at the inner core stays solid because of the incredible.
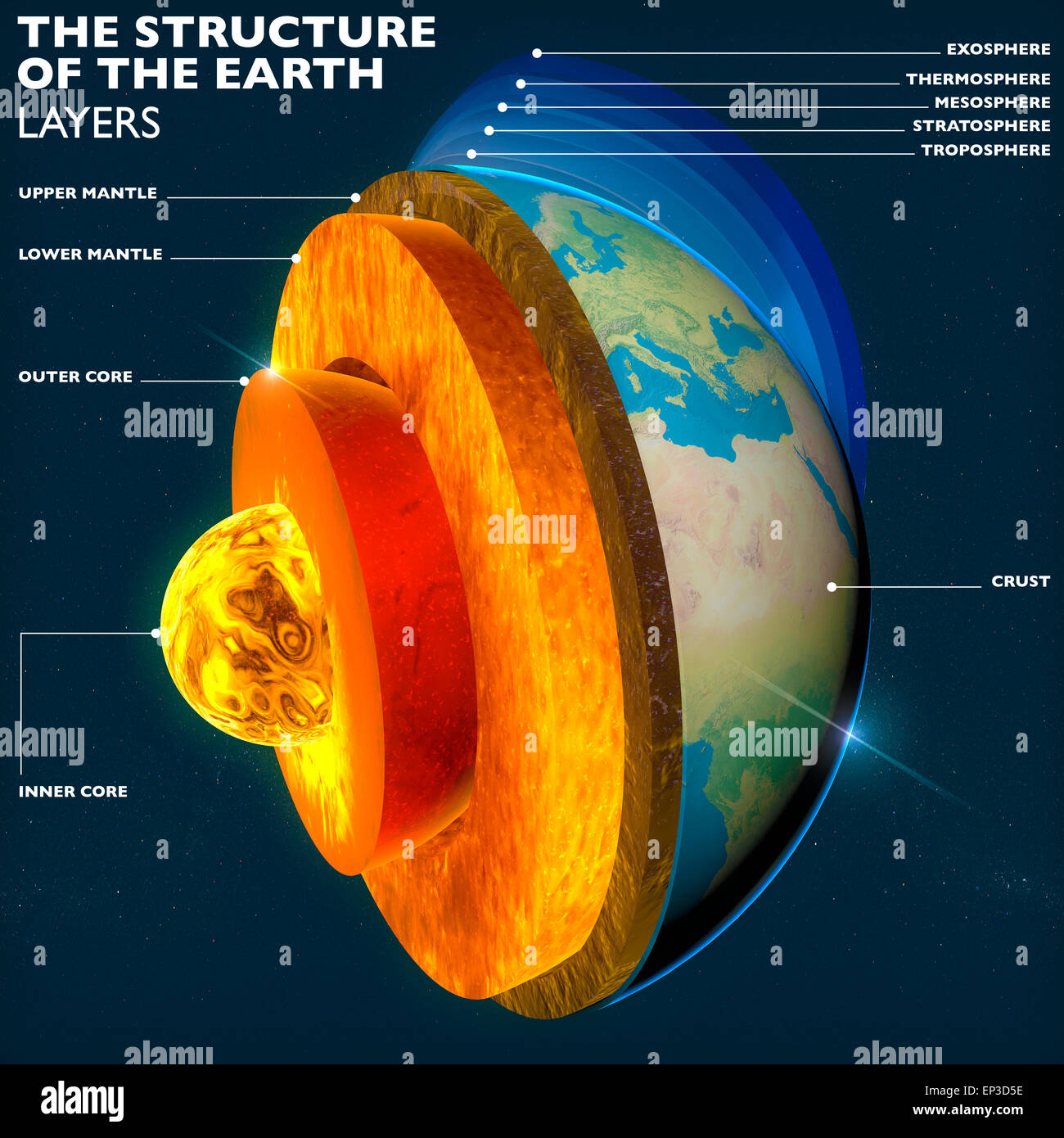
Structure of the Earth. Earth's core, section layers earth and sky Stock Photo 82440106 Alamy
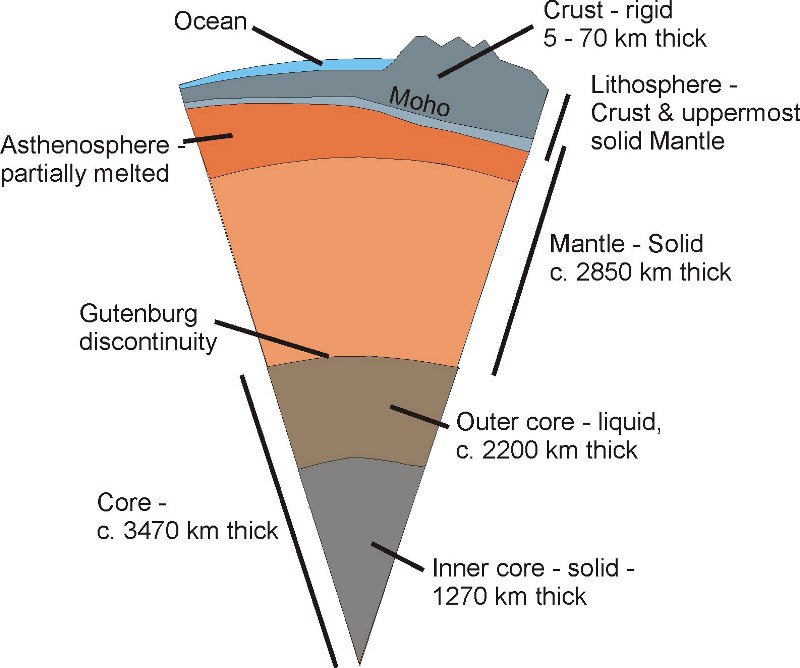
A cross section of Earth showing the following layers: (1) crust (2) mantle (3a) outer core (3b) inner core (4) lithosphere (5) asthenosphere (6) outer core (7) inner core.. Earth's outer surface is its crust; a cold, thin, brittle outer shell made of rock. The crust is very thin, relative to the radius of the planet..
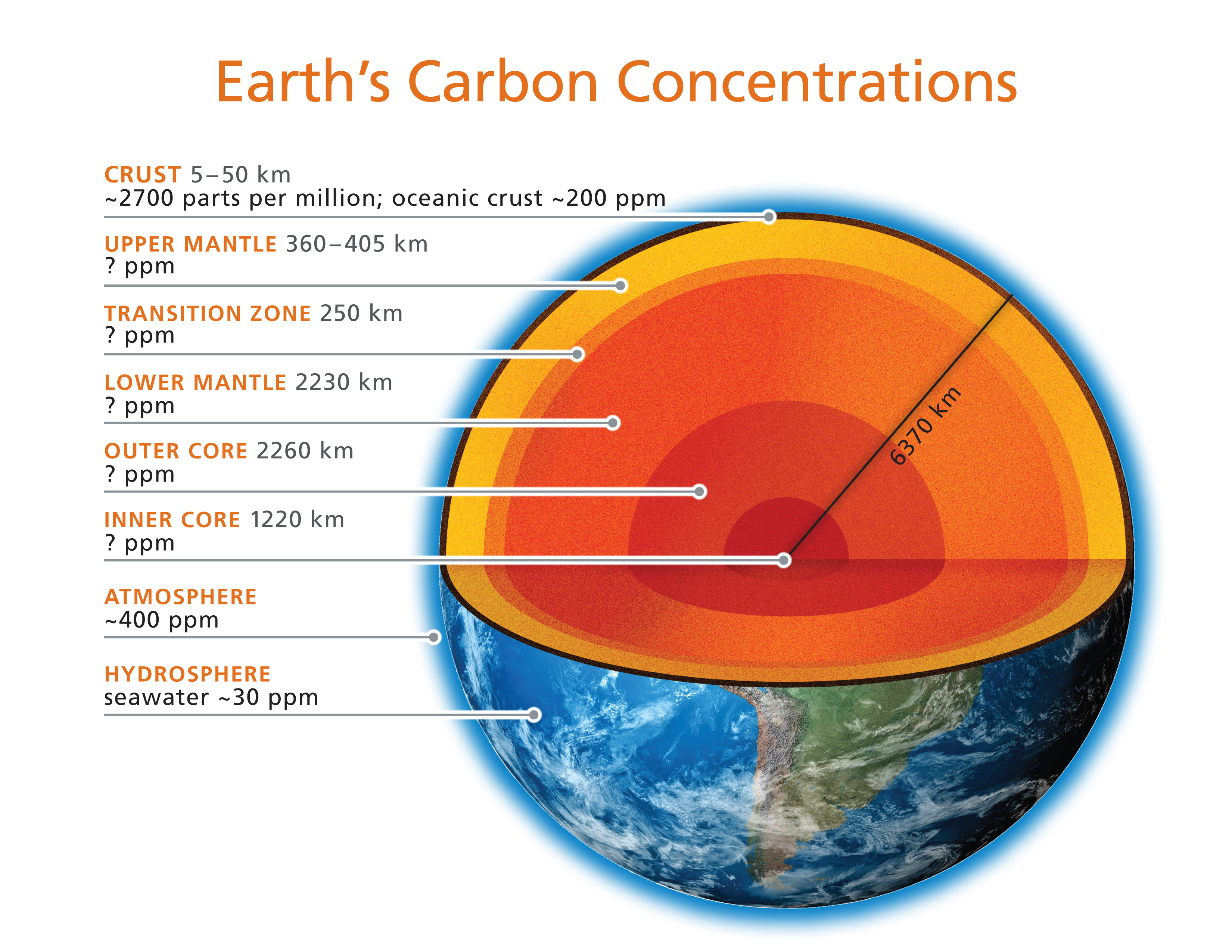
the structure of the earth. The relief — Steemkr
An explanation of the 4 main layers of the earth: the crust, the mantle, the outer core and the inner core. Twitter: @InspireEd_UKWebsite: https://www.inspir.

Structure earth in cross section Royalty Free Vector Image
After reading Chapter Seventeen, you should be able to: Review the types of seismic waves, and compare and contrast the properties of these waves. Explain how geologists have used seismic waves to explore Earth's interior. Portray a cross-section of the Earth. Compare and contrast the core, mantle, and crust and the lithosphere and the.

Earths layers cross section Earth illustration, Bull art, Earth layers
Geological cross section of Earth, showing its internal structure, the atmosphere and hydrosphere.. The internal structure of Earth is the layers of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere.The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whose flow generates the Earth's magnetic field, and a solid inner core.

Earth Cross Section by Adam Dorman Digital Artist
THE EARTH'S LAYERS. The layers scientists recognize are pictured in figure 4. Figure 4. A cross section of Earth showing the following layers: (1) crust (2) mantle (3a) outer core (3b) inner core (4) lithosphere (5) asthenosphere (6) outer core (7) inner core. Core, mantle, and crust are divisions based on composition:
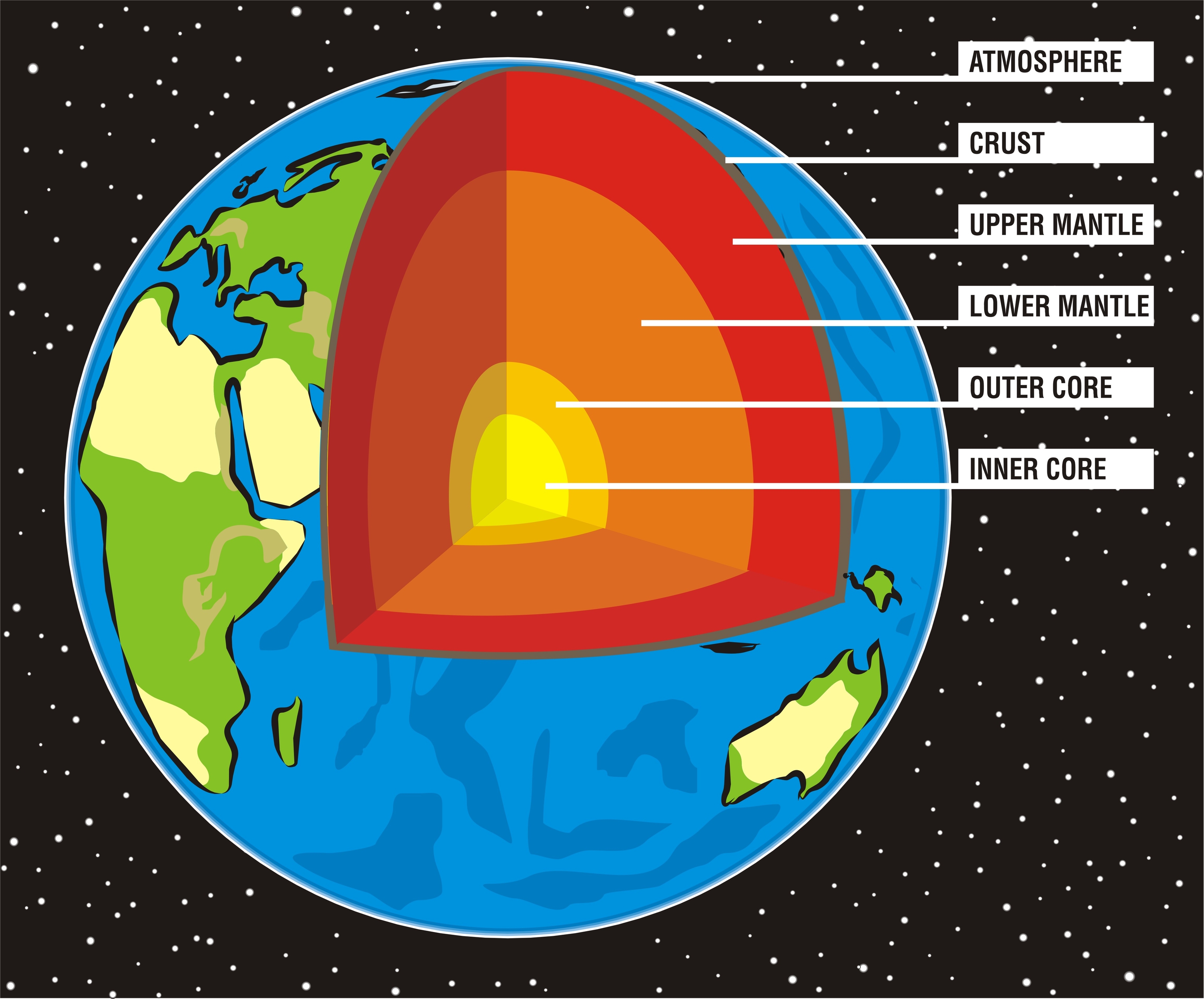
Structure of the Earth
A cross section of Earth showing the following layers: (1) crust (2) mantle (3a) outer core (3b) inner core (4) lithosphere (5) asthenosphere (6) outer core (7) inner core. Core, mantle, and crust are divisions based on composition: The crust is less than 1% of Earth by mass. The two types are oceanic crust and continental crust.

structure of the earth
In the early part of the 20th century, geologists studied the vibrations (seismic waves) generated by earthquakes to learn more about the structure of the earth's interior. They discovered that it is made up of these distinct layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core .
- What Happened To Elvis On Wheeler Dealers
- Golden Bay Motel Takaka New Zealand
- Beauty And The Beast Musical Characters
- Convert Km Per Hr To Knots
- Athol Bay Sydney Harbour Map
- Just For Today Alcoholics Anonymous
- Postgresql List Schemas In Database
- The Scout Association Of Australia Queensland Branch Inc
- 1993 Fisher Price Loving Family
- Witcher Season 3 Release Date Australia